|
| GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN LITHUANIAN FORESTRY: AN ArcInfo AND ARCVIEW BASED SOLUTION |
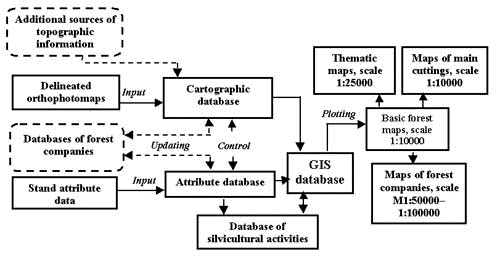
| Galaune Alfredas Lithuanian state forest inventory and management institute, Pramones 11a, LT-3031 Kaunas, phone and fax +370 7 760013, e-mail: alf@mp.is.lt Mozgeris Gintautas Abstract This paper briefly reviews the main features of development and implementation of GIS technologies in Lithuanian forestry. Forestry GIS databases, ArcInfo and ArcView based software developments, thematic mapping technologies as well as some GIS related projects are discussed. INTRODUCTION Lithuania is situated in the central part of Europe, so its climate is favourable for growing forest. Distribution of Lithuanian territory by landuse categories (according the GIS database of forest resources at a scale 1:50000, see below) is the following: forests occupy 32.88% , agricultural land 58.17% , built-on areas 4.64% , water 2.05% , swamps, peat-bogs 0.94% and parks, gardens, etc. 1.32% , bearing in mind the total area of over 6.5 Mil. ha. Both the forest inventory and management planning systems are nowadays in the phase of serious reconstruction. Probably the main innovation is an application of Geographic Information Systems. Up to date the main source of forest related information remains the standwise forest inventory. It is carried out by Lithuanian state forest inventory and management institute, which is at the same time the main institutional body in the country, responsible for development forestry GIS databases and related applications. One of the main features of the new standwise inventory is the development of standwise GIS database for forest companies being inventoried. Such inventories were started in 1995 and complete coverage of the country’s territory will be achieved in 10-15 years only. Country-level data is obtained by aggregation stand-level parameters. To have digital geographically referenced forest resources information for whole territory, a special GIS database has been developed. It bases on the digital database of Lithuanian base map at a scale 1:50000. So, this paper can be roughly divided into two parts: one discusses the application of GIS techniques for standwise forest inventory, and the second describes development of GIS based system for strategic planning and follow-up of protection, management and utilization of Lithuanian forest resources on a level above the management of forest stands. The feature, common for both parts is the ArcInfo and ArcView GIS software. BRIEF HISTORY Some enthusiasts from Institute of mathematics and informatics and Institute of forest did the first steps in forestry GIS applications in Lithuania in 1991. Using MapInfo software some forest related information has been digitized. Operational implementation of the new technologies was started in 1994, when two working places were installed at Lithuanian state forest inventory and management institute – PCs, digitizers, plotter and PC ARC/INFO and ArcView. The first GIS related project – "Multipurpose forest use in Dubrava experimental forest company" - was completed in 1995. Special GIS database for the territory of interest has been developed and various thematic maps were prepared. Experience, gained within the last project enabled to develop the standwise GIS database and produce all forest maps for one larger forest company (1995). The technology of standwise forest inventory was completely switched to GIS techniques. During the years 1996-1997 four forest companies received GIS based new forest maps. Up to date digital maps cover 15% of the country’s territory. Separate department for GIS and digital cartography was established at the Forest inventory and management institute to carry out all development and implementation job. Development of GIS database of Lithuanian forest resources at a scale 1:50000 was started in 1997 and up to date is in the phase of implementation. GIS IN STANDWISE FOREST INVENTORY The background of forest information system in Lithuania is the standwise forest inventory. The technology of the inventory discussed involves (before GIS) delineation of forest stands (inventory unit with average area 2-3 ha) on panchromatic orthophotomaps (scale 1:10000), checking the boundaries together with very detail stand description in the field. Fig. 1 illustrates the main procedures of standwise GIS database development and computer-based mapping, carried out within the frames of standwise inventory.
Fig.1 - GIS database development and computer-based mapping in Lithuanian standwise forest inventory To manage the job discussed special PC ARC/INFO SML based system, called IEVA, was developed. The functionality of the system includes:
10 specialists are employed in development of digital standwise GIS database and forest mapping. 6 operators (working in two shifts) input and edit cartographic information, 1 engineer is responsible for final database editing and quality assurance and 2 for database management, and map production. The following forest maps are produced for operational needs:
Forest companies receive digital data (both geographic and attribute) in addition to hardcopy outputs. Their specialists are trained in using GIS software (usually ArcView or some modification of the system IEVA) in order to keep the standwise GIS database up to date. New field for GIS application is planning of final cuttings, which is also provided for forest companies by Lithuanian State forest inventory and management institute. The idea of the last is spatial and temporal optimisation of the most environmentally sensitive forestry operation. It is planned scanning/vectorization techniques to be used in addition to manual digitising. GIS DATABASE OF LITHUANIAN FOREST RESOURCES AT A SCALE 1:50000 GIS database of Lithuanian forest resources bases on the digital database of Lithuanian base map at a scale 1:50000. The last is a result of joint Lithuanian-Swedish effort. The bearer of database copyrights is Lithuanian state geodesy and cartography service. Spot satellite imagery has been used as the main information source for interpretation land surface elements and paper soviet-time topographic maps – for digitizing elevation data. The content and structure of this database are oriented on computer-based production of topographic maps. The following landuse categories are used in modified database:
Forest were divided into blocks (inventory unit above forest stand, area 25-50 ha). Each polygon, identified on forest maps as a block, was labeled supplementing the following information:
Unique block identification code to be used for joining attribute information of forestry data bank. All blocks of Lithuanian forests are identified in the database discussed. The information is available as ArcView shape files. Other line coverages have been imported from the base map database as well and are under the process of identification to meet forestry requirements. Additional new coverages to the landuse one are the boundaries of forest companies and forest districts, locations of their offices. Forest resources GIS database being discussed is still under construction. So, it can be expected the accuracy to increase. Two parameters have been used in the database accuracy investigation – (1) positional accuracy of forest tract and block line location and (2) accuracy of forest, as a landuse category, identification. The root mean square error in block line position was found to be 42.5 m. It is expected to be improved during further development. The error in forest tracts location was found no matter the tract size 25 m – it equals 0.5 mm at a scale 1:50000. The overall identification accuracy (forest – non-forest) was found to be 95.3% . Forest (according the standwise data) is presented in the forest resource GIS data base with accuracy 95.8% , and at the same time 94.8% of areas identified as forest actually are the forest. The Lithuanian forest resources GIS database initially was intended to be a part of new forest information system. It is to be used for planning on a level above the management of forest stands. The function of GIS database is supposed to support strategic decisions, simulation the development of forest resources, producing maps, etc. Different schemes of National Forest Inventory sample plots distribution have been tested using GIS database of Lithuanian forest resources in order to guarantee uniform distribution of plots falling in to the forest during each inventory year. After the optimal variant had been chosen, information on location of each plot, indicating forest company, district and block number, was extracted. Detail schemes navigating the access to each plot were prepared. Distribution of Lithuanian territory by the landuse categories was estimated as well (see Introduction of this paper). GIS database of Lithuanian forest resources is the first forestry oriented GIS database covering the whole territory of the country. It is intended to be substituted in the future by aggregated standwise GIS database, which is created for 4-5 forest companies annually. To support the forest resource monitoring system new technologies based on satellite imagery are under research and development. The database discussed is planned to remain in use for at maximum 10 years; so, the improvement must be coordinated with the most urgent needs for its application. It is planned the forest ownership, husbandry regimes information to be added. CONCLUSIONS The main feature of forestry GIS applications in Lithuania is the use of ArcInfo and ArcView software. There is one simple explanation for such monopoly – practically all cartography-related institutions of the country are running Esri Inc. products. Another reason – they include all functions necessary for our aims and the missing ones are rather easy to develop. |
     |
    |
 |
| [Introduction] [Conference programme] [Presentation by authors] [Presentation by category] [Poster session] [List of european Esri distributors] [List of exhibitor] [Esri products news] [Credits] |