Wetlands on the Web:
Distributing Ramsar Site Information
Center for International Earth Science Information Network at Columbia
University (CIESIN)
Gregory Yetman, Antoinette Wannebo, Maarten Tromp, and Robert Bourdeau.
Abstract
Ramsar sites are nationally designated and internationally recognized wetlands
under the Ramsar Convention. In an effort to meet the Ramsar community’s
data and information needs, CIESIN, a center of Columbia University, is
working to provide access to data and information on these important sites
through the Ramsar Data Gateway. Satellite-derived data products, socioeconomic
information and site-specific data in an integrated database will be made
accessible over the web using ArcIMS and SDE. This paper addresses the
conceptual and technical challenges of distributing tabular and spatial
data and information to a large community with diverse needs.
Introduction
The Convention on Wetlands, signed in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971, is an intergovernmental
treaty that provides the framework for national action and international
cooperation for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
There are presently 124 Contracting Parties to the Convention, with 1072
wetland sites, totaling 81.75 million hectares, designated for inclusion
in the Ramsar List of Wetlands of International Importance. (Ramsar Bureau
web site: http://www.ramsar.org).
Under a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), the Center for International
Earth Science Information Network at Columbia University (CIESIN); an international
nongovernmental organization (NGO), Wetlands International; and the Ramsar
Bureau, the Secretariat for the Convention on Wetlands, are working together
to create an on-line Ramsar Data Gateway to serve as a clearing house for
both official and non-official information on Ramsar sites.
Multidimensional data
Once completed, the Ramsar Data Gateway will enable users to perform spatial
and attribute queries of both Ramsar and related datasets, conduct basic
analysis, display results as cross tabulations and download results over
the web. The Ramsar Data Gateway will present access to multidimensional
variables from the perspective of a user interested in wetland issues.
The multi-dimensionality of the data sets will allow the integration and
linkage of variables, thereby more fully exploiting CIESIN’s data holdings
and facilitating interdisciplinary analysis. The interface will hide the
complexity of the database structure, allowing the user to view the data
holdings as if the collection were centered on their particular question.
For example, a user could query the database to return the sites that meet
the following criteria:
-
Sites with Commercial Forestry as their principle land use,
-
Sites found in countries that are signatory to the International Tropical
Timber Agreement (ITTA),
-
Sites found in countries that have a deforestation rate of over 35% in
1995, and
-
Sites found in countries with a population increase between 1990 and 1995
over 35%;
This query would normally require that 4 separate datasets be consulted.
Using the new data model and associated interfaces, this type of query
will be possible with a minimum of user effort.
Data Model Description
The Ramsar database has been modeled in an Oracle database using a data
model – the Infusion data model, see figure below – developed at CIESIN.
The Ramsar dataset, like all datasets, is a collection of variables. Variables
are a set of values all of the same type, such as numeric, temporal, or
textual. A value can be an individual number, keyword(s), a geographic
location, or a note. Variables of the Wetlands International Ramsar Site
Database include area, wetland type, land use in wetland and salinity.
The variable values of the Ramsar database are organized into a structure
that is referred to as the dimensions of the variable. With a known schema,
the variables in the Ramsar database can be linked together though their
dimensions. For example, a Ramsar site can be linked to treaty information
through the country that a site is contained within. In the earlier sample
query, the relationships of both sites and treaties to countries were used
to identify sites in countries that have signed the ITTA.
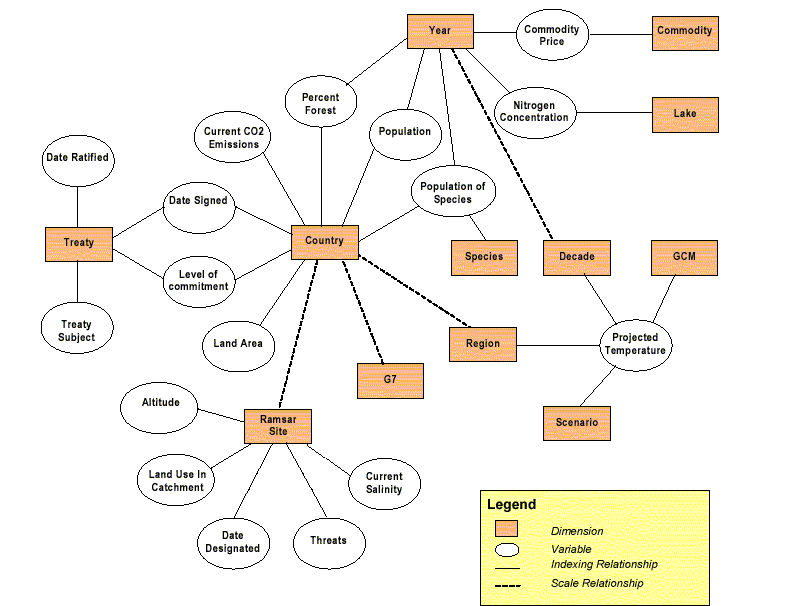
The data model is flexible in the presentation of the information because
it allows users to access multiple units of analysis. If the user were
interested in data related to Ramsar sites, the user could “pick up” the
Ramsar Site box and then the linked variables would be accessible through
their dimensionality. The unit of analysis in this case would be the Ramsar
site. Based on the unit of analysis, the user would then be presented with
a series of tools for selecting objects: manual selection tools and criteria-based
selection tools.
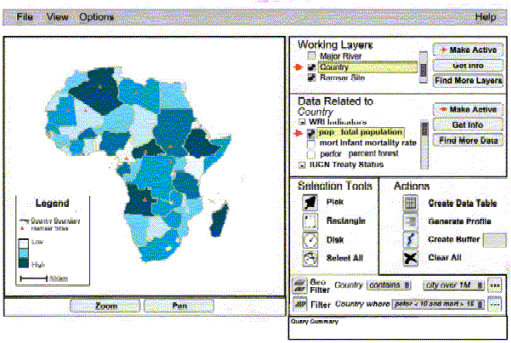
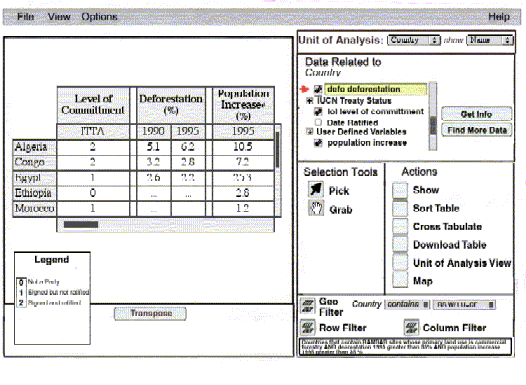
The Multipurpose Graphical User Interface (GUI)
The Graphical User Interface will provide users with a convenient tool
to extract data and information stored in the data model. Multiple data
layers and their related tables/variables can be selected to include in
the data visualization and analyses.
Integration of Spatial Database Engine (SDE) and the Oracle Data Model
SDE will be used to store the spatial data (raster and vector) accessed
through the multipurpose GUI. In this way, the variables will be
stored and managed in Oracle, while only the spatial components will use
SDE. This allows each program to work with its strength – Oracle with Relational
data and SDE with spatial data. Spatial data layers will be linked
to variables as necessary for use in the viewer. For instance, Ramsar
site information (variables) will be stored in Oracle and linked to their
boundaries in SDE via a common identifier. Similarly, country boundaries
will be linked with variables on countries (population data, treaty information,
etc.) through a set of identifiers. In this way, users can take advantage
of the Infusion data model via the GUI to access data. The presentation
will vary depending on the active unit of analysis, allowing the user to
use both spatial- and variable-based criteria to select, view and manipulate
data.
The multipurpose GUI and SDE components of the Ramsar Data Gateway are
still under development. In the interim, we have used ArcIMS and the Ramsar
Data Gateway to provide query and visualization tools to the Ramsar community.
ArcIMS Internet Mapping Solution
At present, CIESIN enables the user community to access satellite-derived
data products, socioeconomic information and Ramsar site-specific data
through a prototype on-line Internet mapping application using ArcIMS.
This application puts the Ramsar site information in a global context of
socio-economic factors such as surrounding land use and population density,
through linking several related datasets. The ArcIMS “HTML Viewer” is used
on the client side.
Currently the spatial and tabular data are not integrated in one data
model. The tabular data is stored in Oracle, and the queries are performed
independently of the spatial representation of the data. The spatial data
is visualized and analyzed using ArcIMS. The primary entry point for this
ArcIMS application is the results page from a query to the Ramsar Data
Gateway via the CIESIN site (http://sedac.ciesin.org/ramsardg).
The Gateway can be used to select Ramsar Sites by querying the Oracle database.
Using the result page there are two main options for further spatial visualization
and analysis. The first is to have global overview of the selected sites;
the second is to start a regional application zoomed to the individual
site.
ArcIMS Server Configuration
-
ArcIMS Version 3.0
-
SUN Solaris (SUN Enterprise Server)
-
Apache web server with Tomcat Servlet
Datasets Utilized
To reduce geometrical distortion, and processing time, the Ramsar sites
are grouped into the 6 Ramsar regions Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America,
North America, and Oceania. The data layers of each of the regions are
in a Lambert Projection. Datasets linked through the Internet mapping application
include:
-
Vector data:
-
The Ramsar site boundaries. The Ramsar site boundary collection, maintained
by UNEP-WCMC (United Nations Environment Program – World Conservation Monitoring
Center) is a collection of boundaries for most Ramsar sites (http://www.unep-wcmc.org).
-
United States Geological Survey (USGS) Hydro 1 km layers. The rivers and
watershed layers of the USGS's EROS Data Center HYDRO1k dataset were used
(http://edcdaac.usgs.gov/gtopo30/hydro).
-
Digital Chart of the World cities.
-
Attribute data:
-
The database of Ramsar sites. The database of Ramsar sites consists
of the core dataset of the Ramsar convention secretariat maintained by
Wetlands International (http://www.wetlands.agro.nl).
The database is composed of coded and keyword attribute thematic information
for individual sites.
-
The Directory of Wetlands of International Importance. The directory, maintained
by Wetlands International, is a collection of one page summary sheets describing
each Ramsar site in a standard format.
-
The annotated Ramsar list. The annotated Ramsar list, maintained by the
Ramsar Bureau, is a collection of short profiles of each Ramsar site (http://www.ramsar.org).
-
Raster data:
-
The Gridded Population of the World (GPW) dataset. GPW is a global
demographic dataset providing consistent population estimates referenced
to a grid of 2.5 x 2.5 minute latitude-longitude quadrilaterals for 1990
and 1995 (http://sedac.ciesin.org/plue/gpw).
-
The USGS land cover dataset. The Global Land Cover Characterization dataset
from USGS EROS Data Center was used (http://edcdaac.usgs.gov/glcc/globe_int.html).
HTML Viewer changes
The default generated HTML Viewer has been customized to enhance the functionality
and “look and feel” of the application. Some of the applied changes to
the viewer are described below.
-
The layout of the viewer was changed. For example, the frames were rearranged
and the legend was split from the layer list so that it would always be
visible.
-
Help pages were added to the viewer. Users unfamiliar with GIS and ArcIMS
need some guidance in the use of the HTML viewer.
-
The JavaScript functionality was improved. Some of the JavaScript functions
can be optimized, such as the source code used to check browser version,
and the function to replace characters in strings.
-
A page was set up so that query coult start the HTML viewer and automatically
zoom to and select sites. This required that the SQL limitation on the
number of OR statements in one query be overcome. This was achieved by
using “Dynamic layer” and AXL “<EXACT>-tag” to visualize selected sites.
-
A legend for the raster layers was added to the viewer. ArcIMS cannot create
a legend for raster layers, so bitmap was created for each raster layer
and added to the legend when a raster layer is visible.
-
The option to download layers was added. Users can download the specific
data layers as shapefiles; this features is not implemented in the default
viewer. Unfortunately, it was discovered that the Extract Server
“sometimes” does not always create zip-files. Periodic restarts of
the ArcIMS services is the only solution discovered to date. Additionally,
ArcIMS does not delete the zip files created for download, so a crontab
demon process was set up on UNIX to delete the zip files.
Gregory Yetman
Antoinette Wannebo
Maarten Tromp
Robert Bourdeau
Center for International Earth Science
Information Network (CIESIN), Columbia
University



