AM/FM Utilities
by: Dalius Radis, Viktoras Bulavas, Kazys Pleskis
Abstract
Maps are one of frequently used information sources in different departments of GSM Operator Company. Using of digital GIS databases and professional GIS analysis tools drastically increases efficiency of planning and presentation activities.
The RTM (Radio Telecommunications Modelling) application was developed in co-operation with "UAB Mobilios Telekomunikacijos" GSM network planners in order to automate their daily tasks and to integrate all computerised workstations of Network Planning Department in to one information network.
Scope
Paper contain general overview of GSM operator tasks, witch can be solved using GIS. Description of information network in Network Planning Department, used data and software. Specified key points and benefits of using professional GIS tools and customised application RTM, for geographic data management and GSM network planning operations. Presented sample maps and drawings.
Preface
GSM service experienced very rapid grow in Lithuania. Two GSM operators "OMNITEL" and "BITE GSM" (UAB Mobilios Telekomunikacijos) now share over 80000 subscribers. GSM networks cover about 60 percents of the country. GSM networks development was one of the fields, where GSM operators where very active these years.
GSM network planners from "BITE GSM" where evaluating different computer technologies to improve their daily operations. They find out, that apart expert systems from Ericsson they need standard commercial GIS technology for geographic information management and based on it customised GIS tools for solving specific GSM network planning problems. "BITE GSM" started the GIS implementation project in Network Planning Department with goal to expand it to enterprise wide geographical information system.
1. Geographic information in GSM operator company
GIS system implemented in Network Planning Department of "BITE GSM" shows that GIS can be successfully used in several departments of GSM Operator Company for decision making and presentation.
Technical department is using GIS for site selection and evaluation, microwave lines planning, real life GSM signal strength measurements mapping, network coverage prediction and analysis. Authorities, marketing and implementation departments require coverage prediction and base site maps.
Implementation Engineers have an opportunity to use customised maps displaying all essential information needed for transmission engineering. Mapping of real life GSM signal strength helps quality control by relating the predictions and reality perceived by customers. Necessary measures can be taken correspondingly, for example change of antennas for re-sizing of cells, use of extra amplifiers or repeaters for improvements of coverage.
Marketing department is responsible for up-to-date presentation and publishing of current status and perspectives of GSM network for customers. Coverage prediction maps can be prepared for publishing using the map sources originating in technical department.
2. Information network and GIS role in it
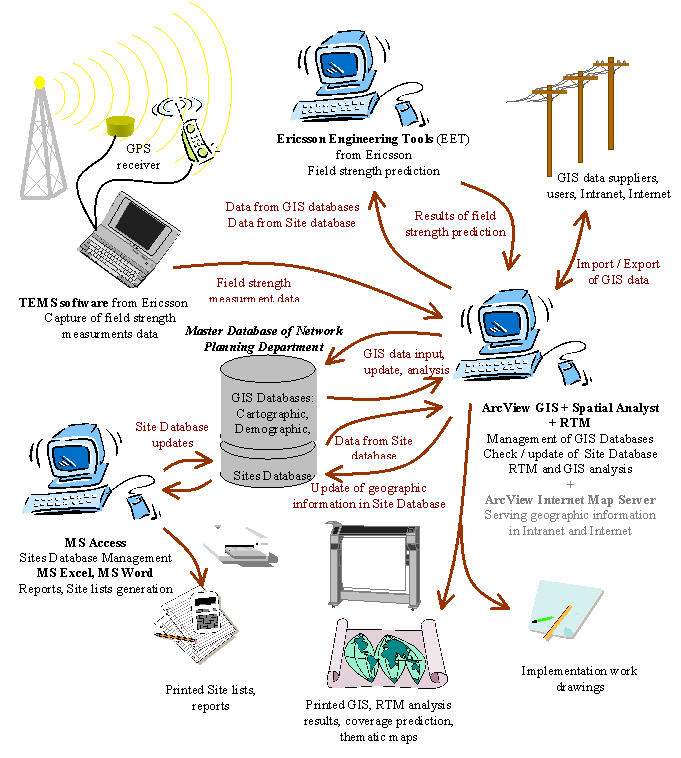
Principal scheme of information flow and processing in Network Planning Department of "BITE GSM" is presented in fig.1. Description of Master database, software used for data processing and information flow is presented below.
As you can see from data flow arrows and short functionality descriptions in fig. 1, GIS software from Esri ArcView GIS with extensions Spatial Analyst and RTM plays very important role in this information network. It acts as main information integration and analysis tool.
Fig. 1 Principal scheme of information flow and processing in Network Planning Department of "BITE GSM"

2.1 Master Database of Network Planning Department
Master Database consist from two types of databases:
- Tabular data databases, such as Sites Database, managed by RDBMS MS Access;
- GIS data databases, such as Cartographic Database, managed by Georelational GIS software ArcView GIS.
At this time there are five main datasets: Sites Database on RDBMS, Cartographic GIS Database, Demographic GIS Database, Field strength measurements data and Field strength prediction data. Capabilities of using digital information (municipal digital map data, demographic office data) from different sources are installed and tested.
2.1.1 Sites Database
Sites database is developed by Network Planners and implemented on MS Access. It contains information about Base Sites location, equipment on the Sites, implementation plans and costs. Information about links between Base Sites -Transmission lines is also stored and managed by MS Access. ArcView GIS is used for update of geographic information (Sites location, Transmission lines length, azimuth).
Structure of Site Database is fully compatible with Site data used in Ericsson Engineering Tools (EET) and ArcView RTM analysis and presentation tools.
2.1.2 Cartographic GIS Database
Cartographic GIS Database was purchased from Lithuanian National Land Survey. It is topographic, vector database created from SPOT images in scale 1:50,000 and covers whole country. Original layers: administrative boundaries, towns, settlements, rivers, lakes, roads, railways, contour lines, forest, land use, power lines, etc. where reorganised and updated using ArcView / Spatial Analyst / RTM to comply Network Planners requirements.
From height information of Cartographic Database (10m contour lines, height points, hidrographic network) Digital Elevation Model (DTM) was calculated by GIS service company GIS-Centras using Esri software ArcInfo and installed in Network Planning Department. Cell size of lattice created from DTM is 50x50 m.
2.1.3 Demographic GIS Database
Network Planners created demographic GIS Database using ArcView. Data from Cartographic database and demographic tables where used. This database contains geographically related data about number of inhabitants in regions, cities, and towns and is very important in GSM network development planning and statistic calculations of network coverage.
2.1.4 Field strength measurements data
Field strength measurements data is maintained by Network Planners and updated from collected field strength measurement data. These data are managed and analysed by ArcView.
2.1.5 Field strength prediction data
There are two sources of field strength prediction data. Preliminary calculations are done by RTM, - advanced, using different methods, with EET. At this stage Network Planners are analysing these prediction results with measurement data and are determining most accurate solution.
2.2 Software used in Network Planning Department
2.2.1 ArcView GIS + Spatial Analyst + RTM
ArcView GIS with Spatial Analyst extension was selected as main platform for:
- Management of GIS databases
- Integration of information in different forms
- Check / update of geographic information in Sites database
- Spatial analysis
- Map and work drawings generation
- Customisation
The key points for such solution where:
- User friendly interface, geographical data management, analysis and presentation tools
- Open architecture
- Ease to learn and administrate
- Direct reading of all vector/raster GIS data formats, GIS data vendors are providing. Therefore is no need to write any converters or to order GIS vendors to do the conversion
- Support of Lithuanian co-ordinate system and GIS data conversion between different projections / datum capabilities
- Support of ODBC connections and SQL queries. Reading data from different RDBMS tables. This functionality is very important for integrating of geographical and attributes data
- Productive, object oriented customisation language Avenue
- DDE and DLL connection capabilities
- Huge users and developers community
- ArcExplorer - Free viewing software of GIS data in ArcView format
- Extendible system. A lot of commercial and not commercial extensions. Ability to enhance GIS and to serve geographical information in Intranet / Internet by using technology from the same vendor Esri (SDE, ArcInfo, ArcView Internet Map Server)
The specialised RTM (Radio Telecommunications Modelling) application on base of ArcView GIS with Spatial Analyst extension was developed using Avenue. The RTM functionality is described in next chapter.
2.2.2 Ericsson Engineering Tools
Ericsson Engineering Tools (EET) is a UNIX based software package based on the product Planet by MSI Mobile Systems International Plc. Product is used by Network Planners for cell frequency planning, advanced coverage prediction calculations.
2.2.3 TEMS
TEMS software from Ericsson is used in Notebook computer for capture of field strength measurement data. These data later on are imported to ArcView and saved in GIS database of field strength measurements.
2.2.4 MS Access + MS Excel + MS Word
MS Access is used for Site database management. MS Excel, MS Word for reports, site lists generation and printing.
2.3 Data flow in information network
Data flow in information network is managed by standard functionality of ArcView with Spatial Analyst and specially written interfaces to EET, TEMS, MS Access. All maps and drawings for final printing are compiled in ArcView.
3. Key features of RTM application
The RTM application is plug-and-play extension to ArcView GIS with Spatial Analyst. If you are network planner and know ArcView GIS, it is very ease to start use RTM just from the box. RTM contains all main functionality, needed for GSM network planning, which couldn,t be found in standard GIS software. All RTM calculations are based on ITI (International Telecommunications Institute) algorithms, standards and recommendations.
RTM functionality includes:
- Operating with geographic co-ordinates. Locating, querying objects (Sites) using longitude, latitude in DMS or DM. Calculating DMS or DM for existing or modified objects
- Specialised stack profiling. (Example of RTM generated profile in App.1)
- Automatic transmission plan generation from tabular Site database (Example in App.2)
- Field strength prediction calculation (Example in App.3)
Great advantage of RTM is: that in ordinary GIS software environment network planner can use all standard professional GIS functionality apart specialised analysis tools. Examples are presented in App.4 and App.5.
Appendixes
App.1 Example of RTM generated profile
App.2 Example of transmission plan automatically generated by RTM from tabular Site database.
App.3 Example of RTM field strength prediction calculations.
App.4 Example of field strength measurement data displayed in ArcView environment.
App.5 Example of GSM coverage map prepared with ArcView for Marketing Department.
Author's Information
Dalius Radis,
GIS engineer of "UAB HNIT-BALTIC GeoInfoServisas";
Certificated in surveying, master degree in information technology, writing
doctor's thesis in metrology.
Laisves pr. 81 - 11,
2022 Vilnius,
Lithuania
Tel./fax. (370-2) 480 718; e-mail: hb-gis@post.omnitel.net
Viktoras Bulavas,
Manager of Network Planners department of "UAB Mobilios Telekomunikacijos";
Certificated in physics, master degree in management.
Zemaites g. 15,
2600 Vilnius,
Lithuania
Tel. (370-2) 232 323; e-mail: tvbu@bite.lt
Kazys Pleskis,
Radio transmission planning engineer of "UAB Mobilios Telekomunikacijos";
Certificated in surveying
Zemaites g. 15,
2600 Vilnius,
Lithuania
Tel. (370-2) 232 323; e-mail: tvbu@bite.lt