Strategic Planning and Marketing Research: Revenue Tool for the
GeoSpatial Industry
The answers to this question in our industry are varied from, "Those things (strategic plans) don't really work," to "We tried that once, paid a lot of money for it too, then it just sat on a shelf collecting dust-nobody really ever looked at it again. We just kept on doing things the way we always had." As the following illustration suggests the road to strategic planning and sales and marketing contains a great deal of obstacles and detours making it difficult for organizations to navigate the business road to revenue growth. Developing highly effective strategic plans provides a map to ease your navigation troubles and warn you about impending business detours you may have to take.
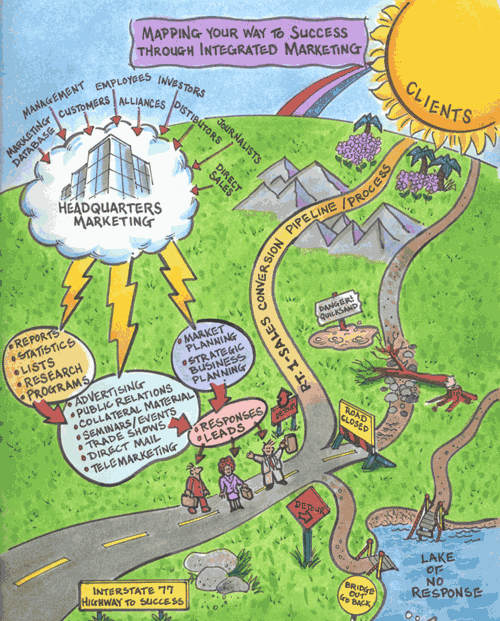
copyright 2001 GLOBAL MARKETING INSIGHT, INC.
| Strategic Plan Components |