Development of Business Application for Area Management
Koji Unozawa
This paper introduces a business application assessment and registration system for Internet providers that has been developed using GIS. Internet providers are required to decide promptly whether or not a communications service can be made available to an applicant who has applied for a new contract. In order to make this decision, they have to analyze the positional relation between the applicant's location and the antenna service area. Using GIS as the core technology, this system adopts ArcSDE for storing a wide-area map database (15GB) covering the Kinki region of Osaka, Kyoto and remaining 4 prefecture, and ArcView3.2 to perform positional analysis of clients and antennas.
1.Background
In recent years, Internet provider business for personal clients has grown dramatically in Japan.
Until a few years ago, the Internet connection environment was largely based on dial-up connection via telephone lines. However, dial-up connection had two major problems, one being the high cost in that it required communications charges in addition to the provider fee, and the other the extremely slow speed of information communications. These problems were solved by Internet constant connection environments such as CATV, FTTH, wireless LAN and DSL, leading to the dramatic spread of the Internet to private homes.
Under these circumstances, Internet providers are exposed to severe competition with each other to acquire new clients. The key to acquiring new contracts lies in how swiftly and accurately information about the services of a provider can be transmitted to clients.
K-Opticom Corporation whose Internet provider business is based on wireless LAN and FTTH, decided that the use of GIS was the best solution to such problems and in 2001 introduced the Area Checking System for checking the Internet service area on receipt of a new contract application.
2.Objectives of the Area Checking System
Before accepting an application for subscription to the Internet constant connection service, it is necessary to check whether the applicant is located within a serviceable area. This process is called the "area check". After the area check has been conducted, data on applicants has to be managed as the client information of each base station.
If GIS were not used, the area check made on receipt of an application would be conducted according to the following procedure:
¥Base Station Management (Preparatory Work)
1.The accurate position of the base station is entered on a paper map.
2.If the base station is relocated (moved to another position or dismantled), its position is revised on the paper map.
3.Client information is managed by each base station (including termination or cancellation of contracts).
EArea Check
1.The applicant's location is defined from a housing map on the basis of the address and is entered on the paper map.
2.The distance between the applicant's location and the nearest base station is measured.
3.A comparison is made with the information on existing clients allocated to the base station within a standard distance.
4.A decision is made as to whether the connection service can be provided, and if it can, the applicant is allocated to the base station.
5.The applicant's data is registered in the client information register of the base station.
@@
If the above work were carried out for each applicant, a great deal of working time would be required to deal with many applicants and it would be impossible to respond to the dramatic increase in the number of clients demanding Internet connection services. The importance of the new GIS-based "Area Checking System (ACS)" lies in enabling applications to be handled more efficiently. The requirements for this system are as follows:
1.The base station serves as a map database and manages information on the clients allocated to it.
2.The applicant's address is entered from the application form and is matched with the address point data containing the coordinates of each house to create point data on the map.
3.When the applicant's location is established, the neighboring base stations are automatically retrieved on the GIS and a list of candidate base stations is displayed. At this time, the distance from the applicant's location to each candidate base station is indicated. It is also possible to refer to the information on existing clients.
4.Approximately 1000 applications per day can be received and processed, and the system operates throughout the year (7 days/week).
3.Outline of Area Checking System
(1) System Configuration
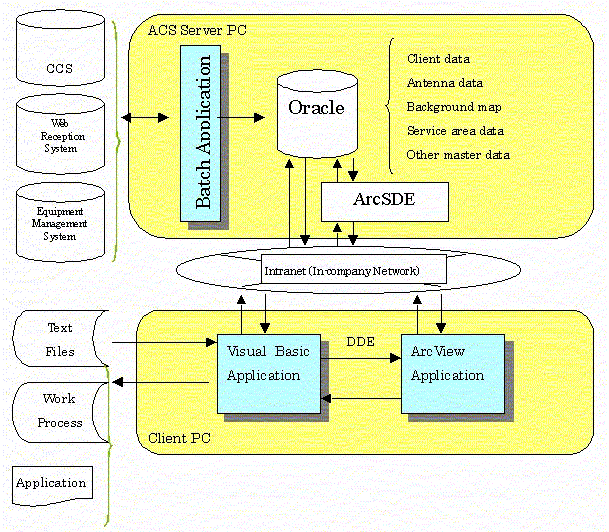
¥The background map, client attribute data, client location data, antenna position data and other master data are arranged in the ACS server PC as the DB server. The batch processing programs created in Visual Basic and C++ for managing related data from the CCS (custmer care system) and equipment management system are arranged as the server application software.
¥The reception and reference system created in Visual Basic and the application software (ArcView3.2) customized for displaying the area check map are arranged in the client PC. In customizing the Area System, the development period was shortened by about 2 months by making the most of the basic ArcView3.2 user interface.
(2) Hardware and Software Configuration
This section describes the hardware configuration of the Area Checking System. The Area Checking System is configured as a client-server system using one PC server as the DB server, and at present there are 30 ACS-dedicated client PCs in operation.
Server PC (1 unit)
CPU Intel Pentium III, 1GHz
Memory 1GB
HDD 64GB
OS Microsoft WindowsNT Server 4.0
DBMS Oracle 8.1.7
ArcSDE 8.0.2
Client PC (30 units)
CPU Intel Pentium III, 850MHz - 866MHz
Memory 256MB
HDD 20GB
OS Microsoft Windows2000
ArcView3.2a
Visual Basic Application
Initially the system was operated with 10 client PCs, but as the number of applicants to be processed per day rose higher than expected, the client PCs were increased to 30 units.
ArcSDE was introduced for the following purposes:
¥Exclusive control in updating
It is essential to have exclusive control of the map data in order to make the area check and register the client data from multiple client PCs.
¥High capacity of map data
It is necessary to store the background map (15GB), including building shapes, covering the Kinki Region (including Osaka and Kyoto and remaining 4 prefecture).
(3) Functional Configuration
The Area Checking System consists of the following functions:
@ Receipt of Application
a) Receipt of new application Input of application data
b) Data update Updating of application data
c) Area check Display of positional relation between applicant and base station
d) Application list output Output of list of application numbers received
A Receipt of Cancellation
a) Registration of cancellation data Receipt and processing of cancellation of application
B Reference and updating
a) Retrieval of conditions Retrieval of conditions of clients and base stations
b) Display of client and base station lists Display of list of retrieved records
c) Display of detailed data on clients and base stations
d) Updating of data on clients and base stations
e) Text data output Output of text data for various purposes
C Data management
a) Updating of master data Code table management
b) Updating of work progress data Data import from other systems
D Batch processing (interface with other systems)
a) Updating of base station data New installation, relocation or dismantling of base stations
b) Updating of client data Entry of contract and termination information
c) Application data import on Web Updating of client table in application data
d) Work progress data output on Web Output of current status data on clients
(4) Example of Display
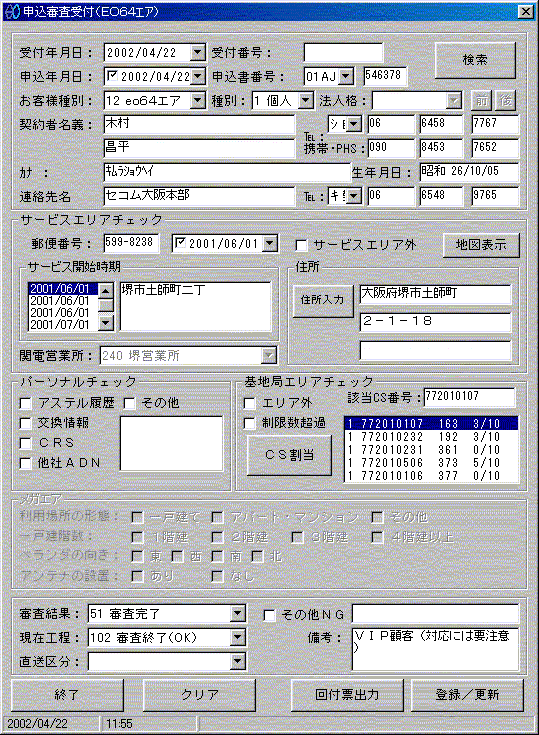
¥Receipt window
This window is used to enter information on receipt of an application, including the address entry field and indication of candidate antenna base stations.
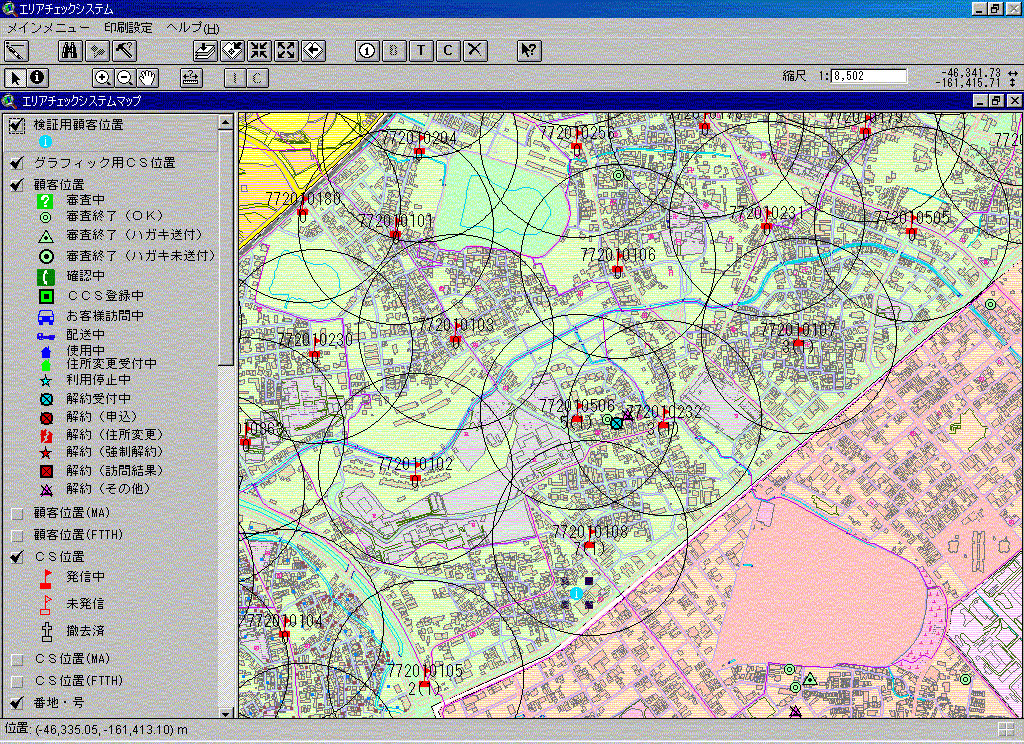
¥Area checking window
This is an example of an area-checking window, showing the positional relation between the applicant and the base station.
4.Outline of Area Checking System
(1) Automatic updating of related data by batch processing
As this system is operated on a 24-hour basis, the following data is entered automatically every evening in batch processing, enabling the operator to conduct the checking work in the daytime based on the latest data.
¥Antenna base station (new installation, dismantling, service-in date, etc.)
¥Client data (contract and cancellation information, etc.)
¥Applicant data on Web
(2) Location registration of applicant by matching location with address point data with coordinates
The position of the applicant's address is defined by matching it with the address table containing the coordinate values of houses. By entering the postal code on the application form, the applicant's address can be selected from the pull-down list on the window to establish the applicant's address and location at house number level, enabling efficient registration of the applicant's location on an electronic map.
If a new address is generated after completion of the address table (due to land readjustment or a newly developed housing area, etc.) and it is impossible to accurately define the address on the address table, the applicant's location has to be determined by reference to a paper map. However, the rate of new addresses is only 2 or 3 percent of all addresses, and therefore does not present a problem.
(3) Exclusive control of map data by ArcSDE
The point data on clients or base stations in the same area may be updated from two or more client PCs. The system is equipped with an exclusive control function for data updating using ArcSDE.
The area lock range for ArcSDE layer updating using ArcView falls within the View display range. Initially, if separate applicants within the same display range tried to register simultaneously from two or more client PCs, it created the problem of the operator often having to wait for a while before proceeding to the next operation. This problem was solved by the method in which the display range is automatically enlarged to a scale of 1/10 during registration processing to cause an area lock, and automatically returned to the original scale after completion of updating.
5.Future Developments
The introduction of the Area Checking System has made the work of handling applications for Internet connection services more efficient, and the system is gaining in importance. In future, there are plans to expand the system through integration with other related systems, ensuring improved user services.
Daisuke Minamiura
K-OPTI.COM Corporation
14-10 5-Chome Nishitenma Kita-ku Osaka JAPAN
TEL: +81 6 6315 7011
FAX: +81 6 6315 7013
e-mail: minamiura@k-opti.com
Koji Unozawa
PASCO Corporation
2-3 2-Chome Nishishinsaibashi Cyuou-ku, Osaka JAPAN
TEL: +81 6 6214 6735
FAX: +81 6 6214 6731
e-mail: kouji_unozawa@pasco.co.jp


