TGS Lite is a complete geoinformation-based application system for small and medium size telecom operators. It has been implemented by several small and medium size telephone operators in Europe. Modified version for a cable TV operator is currently under development.
TGS Lite development has been directly user driven so it strongly corresponds to the real life, everyday practical business needs of telecom operators.
For thee purpose of this paper we define the "small operator" as the operator with up to 100,000 subscribers. "Small operator" can also be the regional unit of the larger operator.
"Medium size operator" is the one with up to or not much more than one million subscribers in one region.
Any larger operator can be treated as a "small" or "medium size" operator if its regional units operate as independent entities, each within above given definitions.
This paper provides an overview of TGS Lite, its functionality, its applicability to the operators business functions, GIS platform and data requirements, environment requirements, and finally issues related to implementing TGS Lite.
While the details of the particular implementation of its business functions may vary, or some of its functions may be outsourced, every telecom operator has at least most or some of the following business functions:
TGS Lite functions have been designed to support many of standard spatially oriented functions within these operators business functions.
Most small and medium size telecom operators have a mixture of legacy and contemporary information systems.
Operating systems: Windows 95 or Windows NT is the desktop OS of choice, although DOS can still be found serving as a legacy application platform. Novell is typically still quite popular as the network server operating system.
UNIX, Windows NT Server, OpenVMS and AS/400 may be present on the servers and minis as well.
Dbase .DBF database structure is quite common among the small operators. Medium operators are more likely to have selected a RDBMS such as ORACLE or INFORMIX.
CAD file formats such as AutoCAD .DWG or Microstation .DGN are likely to be used in the design and engineering departments, but are not integrated with other information system elements.
In short, other than for the Windows as the desktop environment, it is impossible to select one OS - RDBMS - CAD platform and still be able to satisfy more than just a very limited operators.
Therefore, for the development of a widely applicable GIS solution an open GIS platform that can integrate data across such varied portfolio of operating systems, databases and CAD file formats was needed. ArcView GIS from Esri was selected as a powerful and open GIS platform that can support application integration into many required OS, RDBMS and CAD environments for implementation.
To support the operators business functions the following data sets are needed:
Spatial Data
Demographic Data
TGS Lite design goals has been to allow the optimization, e.g. the minimization of investment in data while providing required functionality. For instance, with today�s prices of disk space, using scanned maps catalogs is increasingly affordable. Also, address geocoding support data are more and more common.
Also, not all the data is necessary for the useful start of using TGS Lite. For instance, wit scanned maps, address geocoding system and the locations of distribution points, a customer care department can start using TGS Lite without waiting for the cable graphical data to be entered.
TGS Lite in its current release provides spatial functionality through the common user interface which is the same for all operator business functions. The end user selects from all functions available within TGS Lite the functions he or she needs to perform his or her job or business function.
|
Business function |
Customer contact |
Marketing |
Network planning |
Network management |
Network maintenance field operation |
Network record management |
|
TGS lite |
||||||
|
Exchange "influence" area analysis |
Occasionally |
Occasionally |
Important |
|||
|
Subscriber database management and maintenance |
Important |
Important |
Occasionally |
Occasionally |
Occasionally |
|
|
New service and change of service requests handling |
Important |
Important |
Occasionally |
Occasionally |
||
|
Market analysis |
Important |
Important |
Occasionally |
|||
|
Exchange or RSS location evaluation & optimization |
Important |
Important |
Occasionally |
|||
|
Network records management |
Occasionally |
Occasionally |
Important |
Important |
Important |
|
|
Inter-exchange cables data manager |
Important |
Important |
Important |
Important |
Table: TGS lite functions and their applicability to the operator business functions.
As the TGS Lite grows in the number of functions, that user such common interface is becoming increasingly complex as it offers more choices that any particular user needs for his or her job.
Therefore, TGS Lite user interface is currently being redesigned to be structured more along job-specific modules.
TGS Lite functions, among other, include the following:
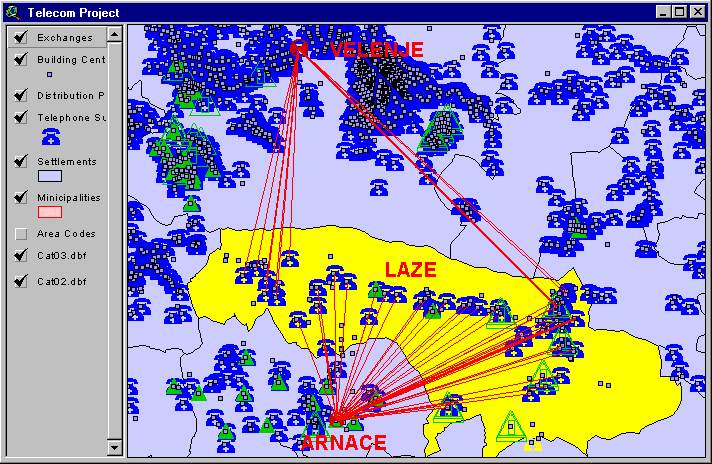
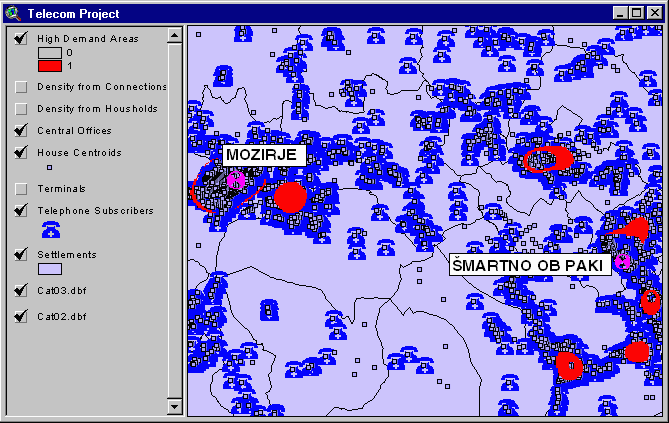
This TGS Lite function analyzes how many subscribers are served by which exchange within a given area. It also provides the mean, shortest, and longest distance to particular exchange within a given area.
This function can also visualize and analyze the locations of all subscribers that are connected to a particular exchange.

Picture 1: Exchange influence area analysis.
Address geocoding provides one more means of customer database verification and quality enhancement.
For the given address where the service needs to be established, entered by the customer contact representative, this function looks for the three closest "candidate" distribution points that may be used to connect the customer and establish service.
This is particularly useful for situations where the customer needs to be connected from the relatively distant distribution point. Using the display of the location and the characteristics of those distribution points as well as other geographic information on the screen (roads, buildings, etc) the customer contact representative can suggest the best and the least expensive choice, generate the work order for the field construction crew, and generate consent or construction permit request forms.
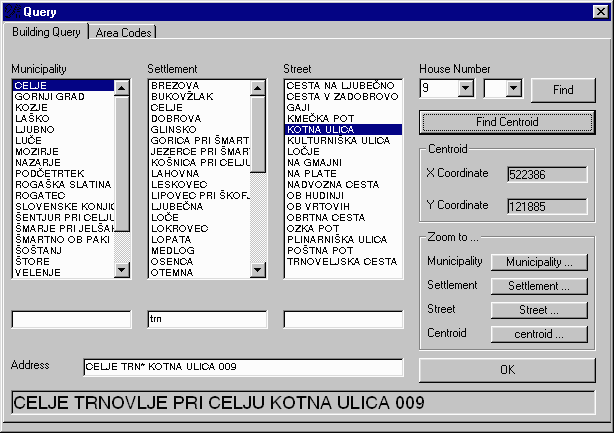
Picture 2
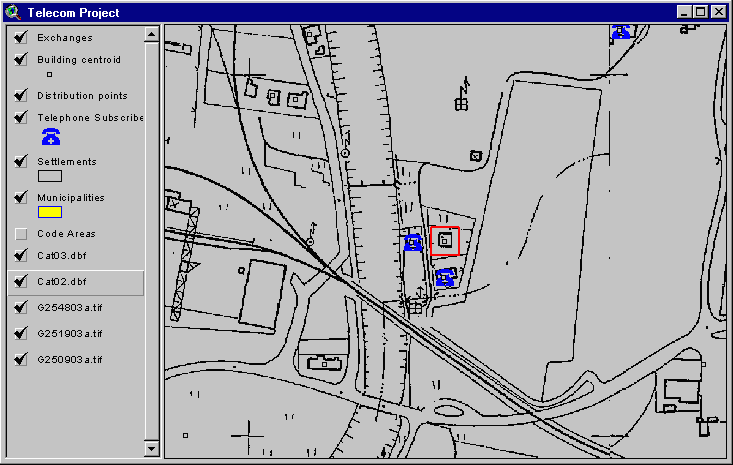
Picture 3
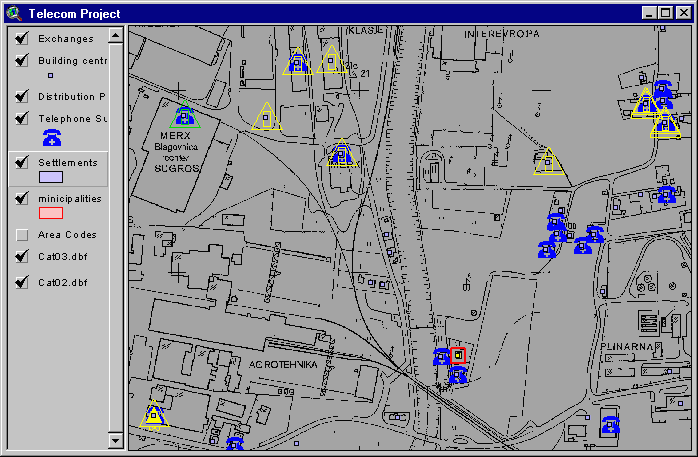
Picture 4
Picture 5
Pictures: This TGS Lite function helps customer contact representatives geocode service request addresses(Picture2), identiify candidate serving DP�s (Picture3), and select the optimal solution, as well as to generate the work order and necessary permit or consent requests (Picture4 and Picture5).
For the selected areas or selected buildings/addresses, the number of households, number of businesses, etc, are given from the database.
For the given area the household density or the population density is computed as a GRID, with the typical cell size of 200x200 meters. In addition to that, other thematic layers can be added, such as: GRID of subscriber distance from the existing exchanges, GRID of subscriber density, GRID of population density, etc. The new potential exchange or RSS locations are evaluated based on these thematic data layers. Alternatively, theoretically optimal exchange location areas are identified.
This functionality requires the archive 3.0 Spatial Analyst module
Picture 6: Exchange or RSS location evaluation
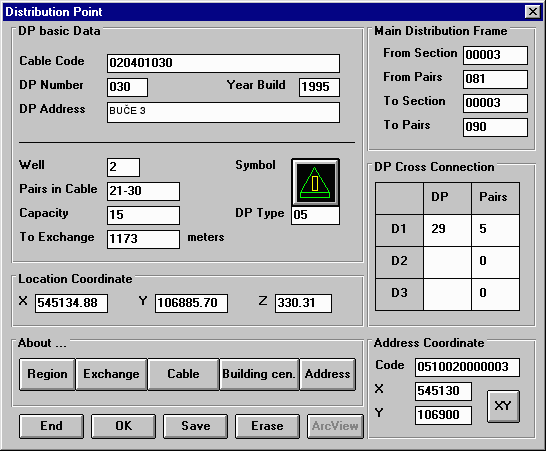
This functionality is specifically intended for the use of the as-built network records management people. The attribute entry/update/change forms are the same as the attribute entry forms in the CAD-based application for network design.
This functionality serves as the geographical data manager and viewer and integrator for the diverse data sets related to the inter-exchange cables. Hot-links provide access to Word documents, Excel tables, CAD schematic cable diagrams, etc. the end user can add, delete, and modify inter-exchange cable data both geographically and as attributes.
The biggest attention should be given to the spatial accuracy and matching success rate of the address geocoding process and the database. The quality of the address geocoding mechanism and database is of the crucial importance for TGS Lite, specially for the customer contact application.
Consideration should also be given to where the raster scanned maps of the area reside: on each desktop or on one server. For larger number of end users the high speed network may be suggested if the scanned maps are all to reside one server.
In the future, the customer relations module may all be implemented with Esri�s MapObjects.
Also, TGS Lite shall be more "modularized" based on the operator business functions.
Korenini Roman,
Gisdata d.o.o.
Saraniciceva 12,
1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia
Phone (+386) 61-314-457
Fax (+386) 61-1323-336
E-Mail: korenini.roman@gisdata.si
Home Page: http://www.gisdata.si