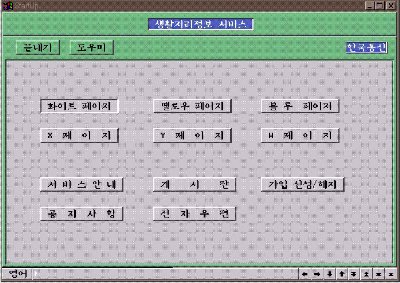
Figure 1. The top menu of GeoMagic
Min Kim Young-Do Joo Byung-Ik Ahn
The purpose of this paper is to review on the technology of spatial data processing in developing GeoMagic, Lifestyle Information Service. GeoMagic is implemented in Korea Telecom in order to provide efficient and various spatial and non-spatial information to public, It is designed to provide geographic information, e-mail, bulletin board, and traffic information service to public using telephone line.
The current service area of GeoMagic is Seoul, the capital city of Korea, revolving five satellite cities and it would be expanded to other major cities. It has been based on hardware environment of DEC ALPHA 2100 and software environment of SDE 2.1, Oracle 7.3 and TCL/TK for implementing of SDE display module and C for implementing PC emulator.
As the information becomes more essential and indispensable to our lifes,
it is needed to provide better and more useful information service to the
public. Especially GIS oriented technologies has been made researches
in order to control spatial information.
Korea Telecom has recognized the importance of GIS technology
since 1986 and has made several efforts to establish GIS technology
in Korea. At first, KT developed TOMS(Telephone Outside plant
Management System) which was designed to manage outside plant
facilities with geographic map data. Secondly the automation rate
of national base map is up to 40% in late 1996, which covers extensive
area of Korea. Thirdly KT has aquired advanced technologies of handling
spatial database and implementing application through the development
and implementation of outside plant facility management system[9,10].
Under this circumstances mentioned above, it is necessary to develop
new application service providing spatial information in order to cope
with rapidly changing GIS world market. The fundamental purpose
of this research is to develop geographic information service using
digital map through the telecommunication network. The main subject of
this paper is the design and configuration of GeoMagic, and the development
of spatial data display module.
GeoMagic Server System provides several spatial and non-spatial information
service. In order to provide spatial informations, GeoMagic has functions
of displaying, querying, and identifying of spatial database using
SDE, Client-Server based on Spatial Database Engine. Also GeoMagic provides
non-spatial information that is divided into textual database related
with spatial database and textual database not related with spatial
database[10].
GeoMagic has six unit modules named whitepage, yellowpage, bluepage, xpage,
ypage and wpage for depending on the intended service. Each page has
different characteristics for various end-users.
Whitepage offers various informations such as business name, address,
telephone number, business hours, schedules for theaters and the map
of the location for each type of business upon the lists of
business classification. Yellowpage makes an offer of addresses, telephone
numbers and the maps of location after user enters the business name and the
related administrative section name. This page can be extended to several
application service such as 911 public service of emergency aids in the United
States. Bluepage supports spatial locational service by user mouse click.
It contains almost same informations with whitepage, but practical usage is
somewhat different. Each user can select more convenient page for himself
or herself[1].
Xpage is focuses on the interests of young generations. It contains
informations of fashion, shopping, and famous places for teenagers. Ypage
is intended for adults while Wpage is for women and both have various
informations upon each interested user groups. GeoMagic permits bulletin
board, and e-mail services. Figure1 shows the top menu of GeoMagic.

GeoMagic has processes based on transaction architecture and each process
is using IPC and transfers data by asynchronous mode. GeoMagic is designed
to deal with database processes of multi-users by single process. Figure 2
shows access network of GeoMagic. Access network of GeoMagic is composed
of the wire system including PSDN which is by X.25 protocol, PSTN in which
users dial up using modem directly, and ISDN, Integrate Service Digital
Network. As a part of the wireless system, GeoMagic has wireless data network
and satellite network. Additionally GeoMagic is interconnected
to EDS(Electric Directory System) for telephone number and address
searching through TCP/IP[18].
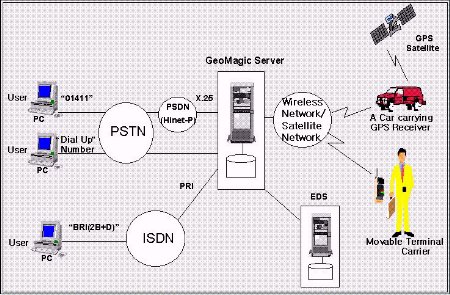
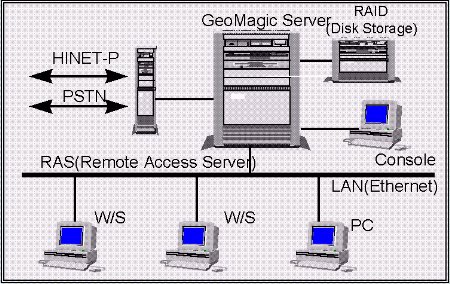
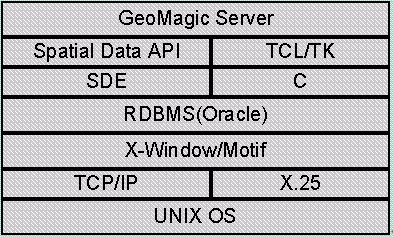
Figure 4. S/W Configuration of GeoMagic
The service area of GeoMagic covers Seoul, the capital city of
Korea and 5 major satellite cities. The main source map is the
traffic map of Seoul published from Chooang Aero Servey and the scale
is 1/10,000. For the purpose of locating service by address
in yellowpage, the brief lot number map of 1/3,000 scale is added on.
Lastly non-spatial data including textual, image, and voice data are obtained
from an on-the-spot survey and automated for Kangnam Subway Station, Hongik
University Subway Station and Apgujung-dong.
The traffic map of Seoul is the thematic map which is founded on National
Base Map, cadastral map and field-surveyed data. This map is updated
annually and also comprises detailed informations of transportation.
The brief lot number map is the thematic map that overlays the cadastral
map which has 14,000 maps for the whole country on National Base Map.
Because of the coordinate discrepancy between the brief lot number map
and the cadastral map, It requires time-consuming mannual work for the congruence
of two maps just like edge matching. It was designed to identify location
by the individual zip code[11].
The dataset of GeoMagic has 150 layers classified by themes. The
schema of layers is as follows ; layer 1 through layer 30 have road
theme, layer 31 through layer 40 have railroad theme, layer 41 through layer 50
have stream theme, layer 51 through layer 60 have contour theme,
layer 61 through layer 70 have administration theme, layer 71 through layer 80
have cadastral theme, layer 81 through layer 100 have transportation
theme, and layer 101 through layer 150 have building theme.
Each layer has attribute tables associated with each layer, pecurially ones to represent
traffic and building themes. Layer 103 to layer 149 have textual and image
data collected from field survey. Figure 5 shows the service area of GeoMagic.
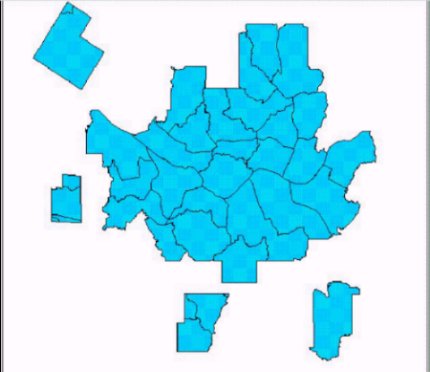
Figure 5. The Service Area of GeoMagic
As shown in Figure 6, GeoMagic consists of 6 systems, (1)Online
Service System, (2)Geographic Data Process system, (3)Operating
and Management System, (4)DB Process System, (5)Application
Service System and (6)EDS Interconnecting System.
(1)Online Service System manages transfer of data through PSDN
and PSTN. It forks out processes to each corresponding system according
to the requests of users. The system involves Network Interface Module, Online
Transmission Module, and Client Request Process Module. Network
Interface Module deals with the connection to PSDN and PSTN. Online
Transmission Module controls transmissions of data. After receiving
request from users, Client Request Process Module links each system
by using Request Reference DB.
(2)Geographic Data Process System is a core part of GeoMagic server.
It has functions of searching and displaying the spatial data,
and GIS arithmetic. To this end, Map Searching Module categorizes
the user requests of map searching and transfers the request
to SDE demon process through SDE API. Then, the structured spatial data
of the searched result is represented to the screen of client emulator
through spatial data display module. Similary, GIS Arithmetic Module and
Attribute Information Process Module send client requests to SDE demon
process through SDE API and transmits the results to clients.
(3)Operating and Management System administers user informations
and collects statistics of GeoMagic with user database. It includes User
Information Management Module, Statistics Process Module, and System
Management Module. User Information Management Module verifies the permission
of users when users dial up in order to connect to GeoMagic server. Statistics
Process Module gathers the statistical data like the amount of time each user
spends on GeoMagic, leading to the rate calculation. System Management Module
administers the whole systems.
(4)DB Process System manages multimedia data e.g. textual, image,
and voice data related to spatial database and queries about
non-spatial informations when searching the spatial database. Non-
spatial database for multimedia service is related to each spatial
feature. When user requests non-spatial informations, DB Process
System transmits the result of structured lists to client.
(5)Application Service System allows bulletin board,
e-mail and traffic information service. It embraces Bulletin
Board Process Module, and E-mail Process Module.
(6)EDS DB Interconnecting System takes charge of the connection to EDS
so as to find a location depending on business name or personal name. It
comprises Administration District Code Module, User Request
Transmission Module, Address Split and Classification Module,
EDS Transmission Module, GeoMagic Transmission Module, and EDS
DB Query Searching Module. When Geomagic user entered the business
name or personal name with detailed administration district,
Administration District Code Module generates administry code for
selection. EDS Transmission Module sends the code and the name to EDS
and receives the resulted information lists of names, addresses, and
telephone numbers. Address Split and Classification Module of GeoMagic
partitions the address by standardized classification for recognizing
spatial location. As a result, GeoMagic can search the spatial location
of user selection by classified address and lot number layer[1].
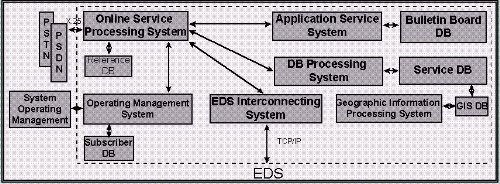
Figure 6. GeoMagic Server System Configuration
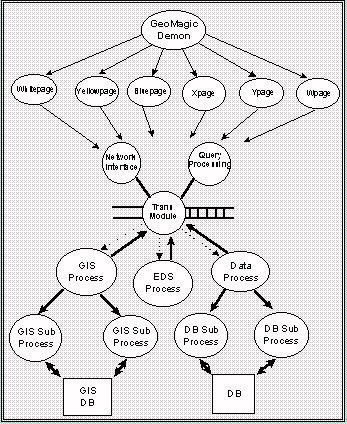
Figure 7. GeoMagic Server Process Configuration
In order to connect the GeoMagic emulator to the GeoMagic Server,
TCP/IP is set up at first. When GeoMagic emulator is executed,
programs concerned with fixing the environment about X-Server
is executed. e.g. the program to load font files, the program to
set hangul, Korean alphabet, on emulator. The LBX(Low Bandwidth X) Server is created,
connected to host system and waiting for transmissions. The LBX
Server transmits data after the connection is settled down between
X-Server and X-Client. The X-Server and the LBXproxy Server transmit
data on low speed network using LBX protocol. On the other hand the
Proxy Server and X-Client transmit data in the same host or on LAN
using X11 protocol at high speed.
When the data is uncompressed at X-Client side, the vector data
of spatial information is displayed on user terminal and waiting
for other actions. If all clients are dismissed, the LBX Server
and the X Server is dismissed.
Figure8 shows the process of connection in order to transmit
the data from X-Server and LBX Server. If the user executes TWINSOCK
and connects to remote GeoMagic Server through modem, the login
process is created in GeoMagic Server. After verifying the user
, the Login Process executes TSHOST of host program and enters
into the SLIP emulation mode. Finally terminal emulator is running.
The TSHOST runs GeoMagic Operating System after the Proxy Server
is in the status of waiting.
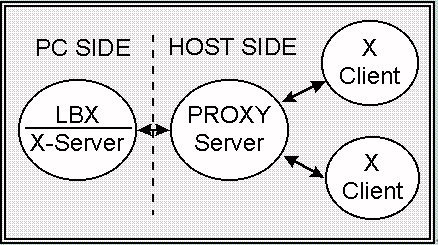
Figure 8. Connection to GeoMagic Emulator
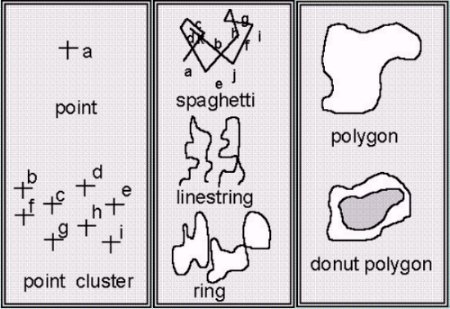
Figure 9. Feature types of SDE
TCL/TK is developed by John Ousterhout in U.C. Berkeley. TCL is
embeddable script language easy to use and TK is a GUI tool kit
providing widgets such as Xt, XView and Motif. Such a characteristic
of TCL/TK facilitates X programming of application much simpler and
faster[15].
Figure 10 shows application development using TCL/TK. TCL allows for not
only providing GUI but also optimizing the programming by improved
reusablilty. It makes application development faster. But TCL/TK
can't access RDBMS or other S/W directly by using related libraries,
and the only solution to figure it out is that the programmer adds
commands to TCL/TK with other corresponding libraries written in programming
languages[4].
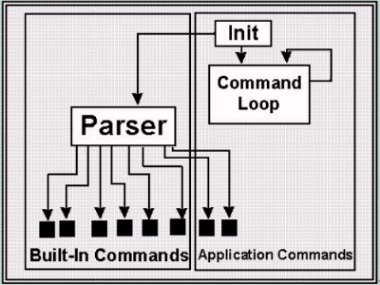
Figure 10. Extension Structures of TCL/TK Application
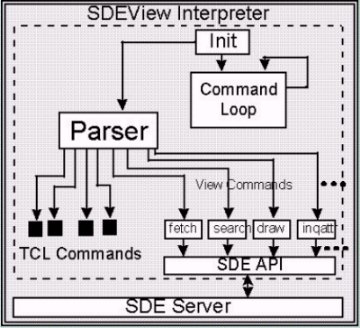
Figure 11. The Structure of GeoMagic Display Module
GeoMagic, Lifestyle Information Service has been developed and
implemented on the circumstances of improved GIS technology in
KT and the necessities to develop new telecommunication service
providing map based informations. This paper centers around configuration
of GeoMagic server, system process design, spatial and non-spatial
database schema, and spatial data display module.
GeoMagic is based on hardware environment of DEC ALPHA 2100 and
software environment of SDE 2.1, Oracle 7.3 and TCL/TK for implementing
of SDE display module and C for implementing PC emulator.
Spatial Data Display Module has basic TCL/TK commands and added commands
that have functions of querying and displaying spatial data. Added
commands using SDE API functions get spatial data from SDE server
and display the spatial data on window widget using X-library.
GeoMagic has six pages of displaying modules and they are classified
upon how to use and who to use. They all have common GIS function
of zooming, panning and identifying and others.
Current service area of GeoMagic is Seoul, the capital city of
Korea and five satellite cities and it would be expanded to other
5 major cities. The scale of base map is 1/10,000 and other non-spatial
data was mostly collected by field survey.
GeoMagic is a kind of PC telecommunication service using modem,
but KT expedites web-based GeoMagic to lead to internet service within this year.
This will enlarge the service scope of GeoMagic. As GeoMagic
spreads out, KT can provide online service for
various geographic information.
[1] B.Y.Ahn, M.Kim, and H.S.Kim, "The Research on Development
of GeoMagic, Lifestyle Geographic Information Service", pp.92-99, Korea
Telecom Technical Review, Dec.1996.
[2] D.J.Maguire, "An Overview and Definition of GIS", Geographical
Information Systems Vol.1, pp.9-20, 1992.
[3] Giri, C.Narayan, "Intorduction to Probability and Statistics", New
York : Marcel Decker, Inc., 1974.
[4] J.K.Ousterhout, "TCL and the TK Toolkit", Addison-Wesley, 1994.
[5] Michael Goodchild, "Accuracy of Spatial Databases", Tayler
Francis, 1989.
[6] W.Richard Stevens, UNIX Network Programming, Prentice-Hall
International,Inc., pp.258-277, 1994.
[7] 1994 International GIS Source Book, GIS World,Inc., Fort Collins, CO
USA.
[8] AGI Standards Committee, "
Dictionary Version 2", Information
and Education Committee Publication, 1993.
[9] A Study on the Network for Logistics Information, Multimedia
Technology Research Laboratory of Korea Telecom, pp.73-98, 1994.
[10] Development of GeoMagic Information System for Living, Outside
Plant Technology Laboratory of Korea Telecom, 1994.
[11] Development of Korean Integrated Land Information System, Ministry
of Internal, National Computerizing Agency, 1993
[12] Electronic Trasfer of Geographic Information(NFT), Part 1, Specification
for NFT structure, 1995.
[13] Introduction to Oracle - SQL/SQL Plus, Oracle, 1994.
[14] Introduction to SDE, Esri, 1996.
[15] SDE Developer's Guide Version 2.1, Esri, 1996.
[16] SDE Programming and Administration, Esri, 1996.
[17] Spatial Database Engine, CADLAND Inc., 1996.
[18] The Development of Electronic Directory Service, Multimedia
Technology Research Laboratory of Korea Telecom, pp.144-150, 1994.
Young-Do Joo
Director/Senior Member of Technical Staff, GIS/GPS Research Team
Multimedia Technology Research Laboratory, Korea Telecom
62-1, Whaam-dong, Yusung-gu, Taejeon, Korea
Telephone : +82-42-866-3190
Fax : +82-42-866-3144
E-Mail : joo@geonet.kotel.co.kr
Byung-Ik Ahn
Member of Technical Staff, GIS/GPS Research Team
Multimedia Technology Research Laboratory, Korea Telecom
62-1, Whaam-dong, Yusung-gu, Taejeon, Korea
Telephone : +82-42-866-3203
Fax : +82-42-866-3144
E-Mail : biahn@geonet.kotel.co.kr