James C. Ascough II, Harriet D. Rector, Brenda G. Faber, and David G. Wagner
The Farm Spatial Database Management System: A GIS for Precision
Agriculture
Present day precision agriculture warrants the
necessity of automated systems for managing farm data and associated
attributes. Agricultural producers who use precision farming techniques
are requesting development of GIS software applications to analyze
spatial data. The Farm Spatial Data Management System (FSDMS) is an ArcView
3.1 GIS tool developed to manage and analyze spatially-oriented agricultural
data and facilitate GIS linkage to the USDA-ARS Great Plains Framework for
Agricultural Resource Management (GPFARM)decision support system. The FSDMS
system provides both pre- and post-processing of spatially-oriented GPFARM
data. This paper focuses on general application of the FSDMS system and
describes how it integrates with the GPFARM DSS.
INTRODUCTION
The Great Plains Framework for Agricultural Resource
Management (GPFARM) decision support system (DSS) is being developed as a tool
to provide strategic planning for Great Plains farming and ranching systems
(Ascough et al., 1997; 1998). In
general, GPFARM will allow the development of long-term strategic planning
scenarios in a non-spatially variable environment within defined land
management units. The incorporation or
linking of a geographical information system (GIS) to the GPFARM DSS will
provide the capability to archive, access, analyze and link spatial and
attribute data generated from a variety of sources. A beta version of GPFARM was made available to farmers, crop
consultants, university personnel, and other beta testers in February
1998. This version will evolve to
Version 1.0 of GPFARM in October 1999.
Version 2.0 of GPFARM is to incorporate GIS-based geographical
coordinate data and maps. GPFARM is
designed to draw on many sources for input data and information. In many cases,
the data will be made available in georectified maps with either
latitude-longitude or Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate
systems. Additional data not in map
form for many farm and ranch units are linked to coordinate positions in base
mapping systems. GIS systems are
efficient in storing, accessing, analyzing and displaying this form of
attribute coordinate-linked data to the GPFARM DSS. The strategic planning output from GPFARM is anticipated to be in
the form of tables, reports, and maps.
In order for the map output to be effective for some more advanced end
users, the maps and many of the GPFARM spatially-oriented tables should be in
geographic coordinate systems for insertion into user GIS systems and data
banks.
The objectives of this
paper are to:
·
Describe the development of
a Farm Level Spatial Data Management System (FSDMS); and
·
Show how the FSDMS will
integrate into the GPFARM DSS currently being developed by the USDA-ARS Great
Plains System Research Unit (GPSRU) and Colorado State University (CSU).
VARIABLE RATE FARMING AND RANCHING
Producers who implement variable rate
or precision farming operations use data generated by differential global
positioning system (DGPS) location sensing equipment. Almost all DGPS data are in either latitude-longitude or UTM
coordinate systems. Whether the digital
maps are generated by combine DGPS-controlled yield monitors or the nutrient or
pesticide applications are controlled by DGPS-controlled applicators (driven by
prescription maps), the need for GIS/FSDMS mapping systems is justified. The repository for historical yield maps or
application prescription maps and map-linked attribute data tables is most
efficiently managed by the GIS component of the FSDMS. Additional data are required for modern farm
management. Government programs are in
potential danger of phase-out and profitability of the farm operation in an
open and competitive market makes farming more dependent on combinations of
remotely sensed soil and canopy imagery, as well as more intensive field
scouting for weed and pest problems.
The temporal information requirements and map-based data now required
for modern farming justify an automated system of managing spatial data (maps)
and attribute data (associated data relating to geographic location within a
single map or digital image).
Farming operations can use significant
amounts of nutrients and pesticides.
Leaching of farm chemicals has been proven to contaminate groundwater
aquifers to the extent that drinking water supplies are endangered. Farm/ranch and agrochemical enterprises are
under pressure to increase the efficiency of application. Liability considerations are motivations for
increased documentation of the spatial and quantitative distribution of
agrochemicals and manure in the farm/ranch operation. The FSDMS GIS and linked databases provide efficient means for
storing the temporal, spatial and attribute information associated with the
application of agrochemicals.
Historical field data for nutrient, pesticide, and other input
applications; yield tracking; and for crop rotations can be mapped and linked
to additional attribute data relating to specific fields or changes in field
boundaries. Farm/ranch operations which
use trend information from year-to-year for decision making and for
documentation for governmental programs require a system of mapping with a
georectification of coordinates so that all mapping is on a common coordinate
system. Co-registration of any map
throughout time is assured through georectifying all maps to the same
coordinate system. Using a GIS with a
common coordinate system allows interchange of the farm maps with any other
mapping system or map user whether another farmer, researcher, agribusiness or
government program officer. The FSDMS
should have the capability to georegister any map to a common mapping
coordinate system.
FSDMS SCOPE AND OBJECTIVES
The FSDMS has been developed ArcViewTM
GIS software with customizations based on the AvenueTM macro
language furnished with ArcViewTM.
FSDMS will be applicable for use by the GPFARM DSS (Version 2) and also
as a stand-alone software module. FSDMS
is currently being developed by a team of USDA-ARS GPSRU scientists and
cooperators as an independent GIS module for linking to the GPFARM DSS. The FSDMS development team is training
selected users and testing the software with actual farm data. The FSDMS will also provide an independent
platform for general farm producer and agribusiness industry use. Future programming, evaluation and testing
will be completed in a collaborative environment between the USDA-ARS GPSRU,
producers, crop consultants, agribusinesses, and other GPFARM evaluation team
members. There are three primary
objectives for development of the FSDMS:
Objective 1
The FSDMS consists
of a multi-functional system that:
·
Provides an interface (I/O)
between users, hardware, and programs;
·
Provides management of
spatially referenced data; and
·
Provides interpretation of
georeferenced spatial data, and links the program to other programs that
provide additional data assessment and interpretation (e.g., GPFARM and previously
developed prescription farming modules).
Objective 2
The FSDMS provides a tool for spatial data storage,
indexing, analysis, output and transfer of information and data between
farmers, consultants, researchers, suppliers, and government agencies.
Objective 3
The FSDMS provides a support
mechanism for linking to prescription development modules and for developing
mapping products for application of prescription and variable rate application
farming.
The ArcViewTM GIS
software and associated database and related independent programs running in
conjunction with ArcViewTM through DLL, OCX, and ODBC links are
being used as the development software.
Hardware platforms are personal computers (PC’s) running Microsoftâ WindowsTM 95/98/NT operating systems. Data input will include GIS maps and
databases relating to cooperator test farms in addition to USDA and CSU
research farm data.
FSDMS
CAPABILITIES
Generic Spatial Data Management Tool
The FSDMS, as a
spatial data management tool for farm operations, is compatible with the
strategic planning aspect of GPFARM.
The FSDMS will also be compatible with a short-term management version
of GPFARM if this capability is implemented in the future. The FSDMS also acts as a separate component
for farming operations providing mapping technologies, data analysis and
storage of maps and related attribute data in GIS data tables. The FSDMS provides the following functions
to a farmer:
·
Allows use of differential
global positioning system (DGPS) data for on-farm mapping or acceptance of DGPS
signals for modifying or creation of georectified data that can be converted
into map layers;
·
Accepts georectified maps
from outside sources including combine yield maps, soil sampling maps, field
boundary maps, and weed-pest infestation maps;
·
Acts as an information and
record keeping manager for spatial and attributal map layer data;
·
Provides spatial data
analysis tools providing partial GIS functionality specific to farming
operations; and
·
Provides GIS neighborhood and overlay capabilities.
Archive for Short
and Long Term Data Storage
The FSDMS
provides spatial database capabilities for storage of farm records related to
spatial data and farm operations. Much
of the information record keeping is related to spatially oriented
operations. Examples include:
·
Long term data storage maps
including base farm maps, soil maps, landscape maps, wetland maps, permanent
field boundaries, access roads, and utilities;
·
Shorter term data storage
maps including annual field maps, yield maps, irrigation distribution and
application maps, crop records and maps, and animal records and grazing maps;
·
Management records such as
environmental conditions, weather information, crop damage, pest records and
maps, fertilizer and farm chemical application records and maps, and flood
maps; and
·
Rental land mapping and
field boundary mapping.
Information Tool for
Compliance
Farming operations involving farm
chemicals and farm byproducts involve liability, hazards to employees, impacts
on land and waterways, and impacts on surrounding lands (e.g., adjacent rural
subdivisions). Farm operation records
and map information storage, retrieval, processing, and output will be provided
for:
·
Chemical and nutrient
application maps and associated data;
·
Soil erosion compliance
through crop maps, crop rotation maps, and land contouring operations;
·
Tillage maps and associated
data;
·
Information analysis and
report preparation; and
·
Electronic transmitting and
information distribution capabilities.
GIS for Analytical
Use
Farm operations require processing
of raw spatial data and analysis of spatial information for management of the
farm enterprise. The FSDMS:
·
Provides capability for
neighborhood-type GIS analysis;
·
Provides capability for
overlay-type GIS operations;
·
Prepares map and table
preparation for printed report outputs;
·
Provides data input from a
variety of sources including DGPS point, scanned aerial photography, digital
georeferenced maps from a variety of sources, tabular data input by crop
consultants and the farm operator, and GIS data layers and tabular databases
from other GIS program modules;
·
Allows data transparency
through the use of common geographic coordinate systems; and
·
Routes data input and
output through the Internet or modem-based electronic data transmission.
Farm Query Tool
Although previously mentioned as an
FSDMS capability, the importance of data and information query is a significant
component of the product. Ease of
interaction with both maps and tabular data will be provided to the user.
Spatial Data
Interface for GPFARM Version 2.0
The FSDMS will act
as a linked module to GPFARM and provide the following functions:
·
Spatial data maps and
tables are most efficiently stored in a GIS.
Georeferenced information needed by GPFARM can be accessed and stored
within the GIS function of the FSDMS.
·
Mapping and printing
engine.
·
Spatially distributed
statistical data analysis.
·
GIS overlay and
neighborhood functions for spatially mapped data.
·
GIS charting and graphing
engine.
·
Spatially distributed
database access and table joining to GPFARM database tables.
·
Linking to precision
farming map development or prescription development modules for importing into
GPFARM.
FSDMS USER FUNCTIONALITY LEVELS
Definition of
Function Levels
Effective use of the FSDMS requires that different levels
of user experience with computers and the product be considered. Four levels of use or computer literacy will
be provided based on the following criteria.
All levels of use expect that data storage, query, analysis, and output
will be required; however, the interface and help screens provide different
levels of information access and analysis sophistication, from elementary
analysis to complex spatial analysis and data table management.
Function Level 1
An entry
level user is presumed to be someone interested in elementary mapping (i.e.,
simple map and report output and archival of farm records and maps) and spatial
data storage/analysis in a simple georectification coordinate system, including
a farm-based grid system. FSDMS Level 1 provides
users the capability to sketch farm layouts and develop databases related to
specific locations on the farm layout. Users have the choice of either
creating a sketch of the farm on a blank screen or creating a sketch on top of
an aerial photo, as shown in Figure 1.
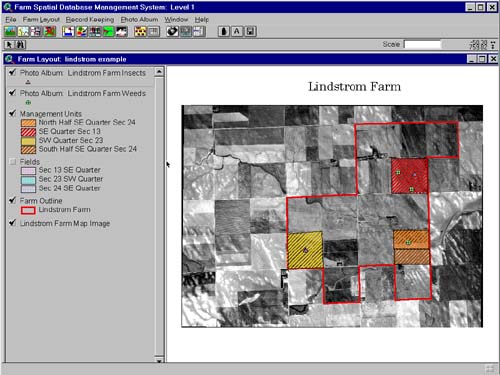
Figure 1. Lindstrom Farm (Eastern CO) Outline Sketched Over Aerial Photo
When the farmer tills the fields or “scouts” the crops
for weeds and pests, the digital field image can be annotated on-screen and
associated data stored in image-related databases tied to the image within the
FSDMS (Figure 2).
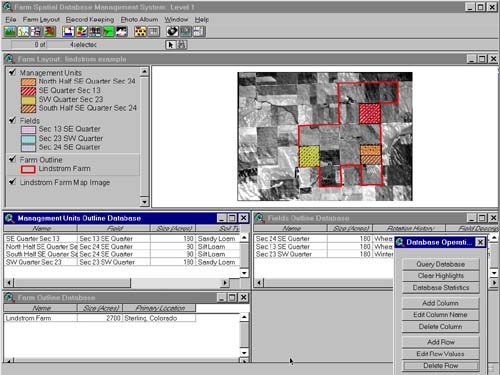
Figure 2. Lindstrom Farm Databases
Crop yields can be entered by field into the image-linked databases. Additional information relating to soil fertility, crop yield,
government program controls, and crop production costs can be entered into
conventional PC-based database software programs and linked or “joined”
electronically to the image-linked database tables. This is the most elementary of the FSDMS functions, or Level 1
functionality. Specific features at
this level include the following basic functions of interest to all users:
·
Based on ArcViewTM
commercial off-the-shelf GIS software ;
·
User-friendly for shortening
the learning curve of busy farmers and consultants whose attention span is
spread across many simultaneous operations during the growing season;
·
Capable of accepting
digital data in the form of maps, images and attribute data through file
transfer protocol (FTP) or modem communications from remote sources;
·
Provides choice of
differing levels of complexity for ease of use from beginner to expert, i.e.,
user can shift to Levels 2, 3, or 4 from this level;
·
Provides “help” or wizard
guides for specific applications or operations;
·
Provides temporal or
historical trending for important parameters; and
·
Provides indexing maps and
tables for ease of review.
Level 2
functionality is a farming operation or enterprise in which the complexity of
cropping or farm size justifies a mapping operation controlled by a geographic
coordinate system such as latitude-longitude or UTM. Any information or any maps that pertain to the farm can be
entered into the FSDMS in the geographical coordinate system thus assuring transparency
between data sources and any single location within the farm boundary. With spatial commonality for all locations
within the farm boundary for any digital map or digital information layer,
historical information can be developed for any location on the farm. The true capabilities for commercially
available geographic information systems can now be applied to the FSDMS and
multiple sources of spatial and attribute data can be entered into the FSDMS. Map-linked data tables can be accessed by
pointing to a specific location on the farm map and any tabular data associated
with the specific geographic location in the farm can be viewed and accessed
for additional analysis. This level
provides all capabilities of Level 1 in addition to the following:
Function Level 2
·
Provides a linkage to
GPFARM;
·
Provides the capability of
DGPS input for on-the-go mapping;
·
Enables farmers to
georectify their own digital geo-locational data and imagery;
·
Provides temporal and
spatial indexing for data tables and maps; and
·
Provides 3-D, contouring,
or color-ramping for contouring elevation and other z-related data;
·
Provides access to
elementary GIS analysis functions.
Function Level 3
Level 3
functionality is an expansion of Level 2 mapping system operations. As large and complex farming operations
adopt modern variable rate application technologies, a spatial data repository
and database system is needed. The use
of combine-based yield data from DGPS locational information and combine output
requires a mapping of the data into yield maps. The yield maps in themselves provide spatial information about
the variable yield across the field.
However, the benefit of the yield map is to provide the producer and
crop consultant with part of a “prescription” for enhancing yields by applying
nutrients or other chemicals to hopefully reduce the cost of chemicals and at
the same time increase potential crop yields.
Precision application may be justified in some cases not by “bottom line”
profit margins, but by government mandates for reduction of soil erosion or for
reduction of nitrates or other farm chemicals being leached to ground waters.
This level provides
all the capability of Level 2 in addition to the following:
·
Provides a linkage to
GPFARM;
·
Provides capability of
interfacing with yield monitoring and variable-rate application equipment. This is a variable-rate application or
precision farming application rate “map maker.”
·
Provides a linkage to
prescription development modules.
·
Provides ease of use in
joining map-linked data tables to external relational databases (primarily PC
databases such as Microsoftâ AccessTM).
·
Offers additional advanced
GIS analysis capabilities including spatial statistics.
Function Level 4
Level 4 functionality encompasses all attributes of Levels 1, 2, and
3. In addition, Level 4 functionality
provides linkage to peripheral models and analysis modules such as neural
network or artificial intelligence prescription farming, i.e., “prescription
development.” In addition to linking to
peripheral modules, the GPFARM DSS will provide an integrated analytical tool
for strategic management of the complete farming operation. Level 4 functionality includes linkage to
GPFARM and other user managed or resource databases through electronic communication. Sharing and transfer of information between
researchers, farm producers, crop consultants, governmental agencies and
cooperative extension, and agricultural suppliers becomes more important in the
future of optimized farm production systems.
The expanding popularity of the Internet and the use of FTP file
transfers between different computer systems operated by the above-named user
groups makes the incorporation of interfaces for ease of transferring
information and data between computer systems via telephone lines. The transfer
of data between crop consultants, producers and USDA-ARS researchers involved
in calibrating and beta-testing versions of GPFARM is necessary and the ability
to transfer mapping and tabular data for use by GPFARM makes the inclusion of
electronic communication paramount in importance.
Level 4 provides research tools for
advanced producers, crop consultants, cooperative extension, and government or
university research. The development of
a prescription module for assessing the spatial characteristics of the farm
portrayed by digital maps, the farmer or crop consultants knowledge of their
farm, and the historical information trends of the data tables and maps of the
FSDMS, becomes an important part of the additional modules or programs linked
to the FSDMS. This level provides all
capabilities of Levels 1, 2, 3, and in addition provides full data
communication for receiving and transferring data to other users, crop
consultants, researchers, and governmental agencies.
CONCLUSIONS
FSDMS will provide an integrated module for interfacing
with GPFARM, a DSS now under development for agricultural resource
management. Farming systems researchers
will be able to use the interface and record storage, record management, record
analysis, and information output to farm simulation and management
modules. Farmers and crop consultants
will benefit by having a system that can receive spatial and tabular data from
remote sources for on-farm analysis and viewing as well as for entering into variable
rate application equipment. GPFARM will
incorporate GIS capability in future versions, and users who are interested in
both GPFARM and precision farming will want linking between both modeling
systems. Transferability and
transparency of data are extremely important to both technologies. In conclusion, the development of the FSDMS
benefits a wide variety of users requiring spatial and temporal data management
and analysis.
REFERENCES
Ascough II, J.C., M.J.
Shaffer, J.D. Hanson, G.S. McMaster, and L.A. Deer-Ascough. 1997. The Great Plains Framework for
Agricultural Resource Management (GPFARM): A decision support system for whole
farm/ranch strategic planning. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. Paper No. 97-5053. Proc. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1997 Annual Meeting,
Minneapolis, Minnesota. August 10-14.
Ascough II, J.C., G.S.
McMaster, M.J. Shaffer, J.D. Hanson, and L.R. Ahuja. 1998. Economic and
environmental strategic planning for the whole farm and ranch: The GPFARM decision
support system. Proc. First Interagency
Hydrologic Modeling Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada. April 19-23.
AUTHOR INFORMATION
James C. Ascough II
Research Hydraulic Engineer
USDA-ARS-NPA, Great Plains System Research Unit
301 S. Howes St., P.O. Box E
Fort Collins, CO 80522
Phone: (970) 490-8371
Fax: (970) 490-8310
E-mail: ascough@gpsr.colostate.edu
Harriet D. Rector
Mathematician/GIS Specialist
USDA-ARS-NPA, Great Plains System Research Unit
301 S. Howes St., P.O. Box E
Fort Collins, CO 80522
Phone: (970) 490-8331
Fax: (970) 490-8310
E-mail: rector@gpsr.colostate.edu
Brenda G. Faber
GIS Consultant
ForeSite Consulting
2151 Evergreen Place
Loveland, CO 80538
Phone: (970) 663-6879
Fax: (970) 663-6879
E-mail: bfaber@foresite-net.com
David G. Wagner
Assistant Professor
Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering
225 Agricultural Engineering Building
The Pennsylvania State University
University Park, PA 16802
Phone: (814) 865-3722
Fax: (814) 863-1031
E-mail: dgw4@psu.edu

