Stephan Kugler
Water Authority of Jordan (WAJ) is restructuring the Amman Water Network within the framework of a 250 mio US$ capital investment program. Dorsch Consult (DC) has been assigned to redesign the congested, most densely populated core of Amman (300,000 population). Time constraints and the pressure to quickly reduce water losses and improve customer services lead to extremely short design periods.
Consequently, DC made use of the existing digital network maps prepared under ARCINFO, combined them with Oracle database systems for customer management, a hydraulic model using PIPE2000 (KYPIPE). ARCVIEW was used as the major working environment not to only graphically presenting results of hydraulic modeling, but to completely re-design pipe networks. Updating of the water demand analysis was done by using actual consumer data out of ARCINFO, automatically assigning demands to network nodes used for the hydraulic modeling. Applying above described approach not only shortened the design period by approx. 30%, but provided as well more accurate, transparent and realistic water network layouts.

Between 1996 and 1997 the Water Authority of Jordan (WAJ) entrusted Dorsch Consult in association with Shubeilat Badran. Associates L.L to carry out a Hydraulic Analysis Study of the Amman Water Supply System. Due to the rapid growth of Amman City and the difficult topography of the city area with extreme level differences the existing water supply system does not allow an efficient water distribution. Currently the water supply in most areas of Amman is based on direct pumping, resulting in high pressures in the distribution network and therewith related high losses. As result of the Hydraulic Analysis Study the restructuring of the Amman distribution network was proposed. In future water distribution will be based entirely on gravity supply. For this purpose the town shall be divided into 42 Distribution Zones. Each of these zones will be further subdivided into Districts, allowing a pressure reduction through Pressure Regulators and permitting better leakage control and eventually resulting in an increased Level of Service.
A multi-donor 250mio US-$ capital investment program is currently being implemented by the Water Authority of Jordan (WAJ) aiming to complete the restructuring of the entire Amman Water Supply System within a 5 years period. 1998 Dorsch Consult in association with Consulting Engineering Center were contracted to carry out the detailed design for the Amman II Programme Area (KfW financed) which includes 7 out of the 42 Distribution Zones. The project area includes the most densely populated part of down town Amman. Due to the urgency to complete the restructuring of the distribution network the earliest possible and the need to co-ordinate between various parts of the Capital Investment Programme the period for the detailed design work was limited to 10 months. The Water Authority of Jordan in recent years has established a GIS based Network Information System for Amman City (ANIS). In order to standardise all ongoing activities related to mapping and network restructuring, all Consultants working under the Capital Investment Programme are obliged to follow the standards set by WAJ. For the Amman II programme base maps of the project area therefore have been received in ARCINFO export format. The Terms of Reference stipulate, that results of the detailed design have to be delivered back to WAJ in the same format and comply with the data base structure of ANIS.
The availability of ANIS - GIS data, which include water network, lots and customer related data allowed Dorsch Consult to follow a different, much more automated approach compared to traditional projects.
The fact, that base maps are received in ARCINFO Export format and the necessity to deliver ARCINFO data and to follow the standards of ANIS, Dorsch Consult decided to use ARCINFO as the main environment to prepare the distribution network drawings for tendering and construction.
The need to generate from the hydraulic modelling software a file format, that can easily be imported into ARCINFO was leading to the decision to use Pipe2000 software (University of Kentucky), which allows to export shape files.
ARCVIEW was used as the major working environment not to only graphically presenting results of hydraulic modelling, but also to recalculate demands for the hydraulic calculations, to perform various types of quality checks, to automatically generate and assign connection details to ARCINFO coverages and to generate all data required for establishing the Bill of Quantity (BoQ). To perform these tasks in an efficient manner missing elements were bridged by developing customised ARCVIEW extensions.
For preparation of the Bill of Quantity, ARCVIEW generated data files were then linked to an MS-ACCESS database.
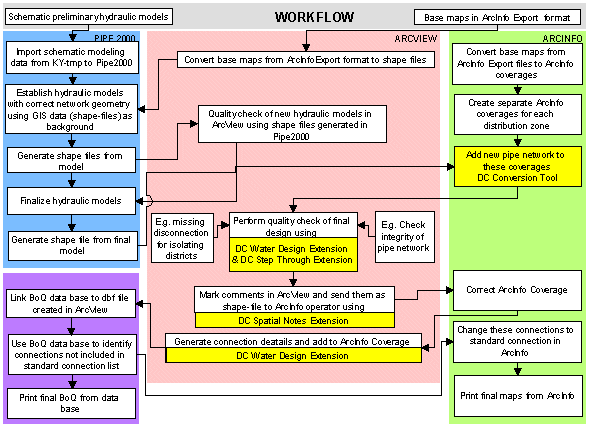
As shown in above flow chart the work started in parallel in Pipe2000, ARCVIEW and ARCINFO. The aim was to minimise the design period by integrating the various software packages.
Preliminary schematic hydraulic models available in KY-TMP format - a previous version of Pipe2000- were imported into Pipe2000. Base maps in ARCVIEW format (shape files) then were used as background image to geometrically adjust these models. After exporting the geometrically corrected models as shape file, a quality check, if all relevant existing pipes and connections were used was then carried out in ARCVIEW. As next step, node demands taken over from the preliminary hydraulic models were adjusted in ARCVIEW with the help of the Spatial Analyser joining actual WAJ customer data with the shape files (demand nodes) of the hydraulic models. These adjusted node demands than were transferred back into Pipe2000 with the help of MS-Excel export and import tool of PIPE2000.
In parallel to the modelling work separate ARCINFO coverages were prepared for each of the seven Distribution zones. Shape files created from the final hydraulic models then were used to add newly designed pipes to the existing pipes in ARCINFO for each of the distribution zones.
These new coverages formed the basis for all further design work for each distribution zone. Considering the size and complexity of the pipe network, the further subdivision into districts and the difficult topography of the area, intensive work in each of these distribution zones was required. Major issues where disconnection’s between distribution zones and district zones, looping of existing minor pipe network not included in the hydraulic models and adjustment of zone boundaries. To standardise all required quality checks and to also permit less experienced ARCVIEW users to perform these tests, an ARCVIEW Extension named DC Water Design and DC Step Through was developed.
In order to reduce the use of print outs and to ease the transfer of information between the water supply Engineers working in ARCVIEW and the ARCINFO operators a tool named DC Spatial Notes extension has been developed. This extension allows to transfer spatial notes into shape files, which then directly can be used by the ARCINFO operators to make changes in the respective ARCINFO coverages.
One of the most time and manpower intensive tasks during the detailed design of a water distribution network, particularly if there is an existing network with different types of pipe material, is the design and labelling of the individual connections and the preparation of the bill of quantity with all required fittings. A tool allowing to automatically assigning the required standard details to each new connection therefore was developed and is included in the DC Water Design extension.Adding the type of standard detail, pipe material and diameters of the various pipes to the ARCINFO files is done in one step.
As a next step this information than has been linked to an MS-Access database generating the bill of quantity for all connections types including all required fittings.
After adding the connection type details final tender drawings were prepared and printed in ARCINFO.
The integration of the various software packages used in the project permitted the automation of various steps of the detailed design of water supply network. Starting from adding new pipes from the hydraulic models to the existing network up to the automatic generation of Bill of Quantity resulted in a substantially reduced design period.
Furthermore the reduced use of paper permitted the project to be accommodated in a much smaller office than usually required for this type of project. An additional benefit is the improved data quality in respect of isolation of new zones as well as network integrity.
Analysing the operational problems of not only Amman but also many other big cities suffering from water shortage, the need for a tool allowing demand oriented operations management under intermittent supply condition using real time processing of flow & pressure data is seen as very urgent.
During this project the first success trial runs of importing entire existing networks from ARCVIEW to Pipe2000 and after analysing back into ARCVIEW have been performed.
In combination with customer data and contour maps this tool will permit to easily create all-pipes models in a very short period. In combination with real time operations data available in GIS a tool for tracing operational problems and identifying shortcomings in existing networks during regular operation shall be aimed for as next step.
The integration of Arcview, ArcInfo and hydraulic modeling software (PIPE2000) only results in productivity gains and shortened design periods, if the whole design process is taylard towards such integration, staff is team-oriented and digital data available in reasonable quality.
Even greater benefits are expected in better construction management and operation of the systems, but have not been analyzed yet.
The inputs of Steffen Macke who just joined the GIS community with his profound programming and analytical skills, dedicated and engated in his work contributed considerably to the success of our work.
Stephan Kugler, Advisor Network Operations, Dorsch Consult