Riccardo
Galetto
Full professor, OOEPE President, DIET - Dipartimento di
Ingegneria Edile e del Territorio Universita’ degli
Studi di Pavia, , tel (+39-382) 505410, galetto@ipv36.unipv.it
Carlo Monti
Full professor , DIIAR Director, DIIAR
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Idraulica Ambientale e del
Rilevamento - Sezione Rilevamento, Politecnico di Milano,
P.za Leonardo da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, tel (+39- 2)
23996240 fax (+39-2) 23996550, direz@idra5.iar.polimi.it
Anna Spalla
Professor, DIET - Dipartimento di
Ingegneria Edile e del Territorio Universita’ degli
Studi di Pavia, tel (+39-382) 505406, spalla@ipv36.unipv.it
Raffaella Brumana
Researcher, DIIAR Dipartimento di
Ingegneria Idraulica Ambientale e del Rilevamento -
Sezione Rilevamento, Politecnico di Milano, P.za Leonardo
da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, tel (+39- 2) 23996533 fax
(+39-2) 23996550, brumanar@idra5.iar.polimi.it
Luigi Fregonese
2nd year Course, DIIAR Dipartimento di
Ingegneria Idraulica Ambientale e del Rilevamento -
Sezione Rilevamento, Politecnico di Milano, P.za Leonardo
da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, tel (+39- 2) 23996533 fax
(+39-2) 23996550, frego@brezza.unive.iuav.it
Abstract
It’s always
more necessary to use Cadastral data to support a
segmentation of users inside the Digital Cartography,
therefore it seems a valid solution to organize a
Relational Data Bank Remote Located access so to allow
the protection, updating and safety of the data, to avoid
duplications which risk to vanify the efforts of
maintaining life-archives and which risk to vanify the
integrated use of data banks built by different local
governments and public bodies distribuited on the
territory.
Through the connection by wire of informative points
diffused in the territory, the GIS on NETWORK Technology
allows the GIS, once structured, to be available from
remote places and from technicians and operators which
use at the different levels the data survey to plan and
project.
It has been studied how the level of data acquisition and
data management can be structurized: from the low level
with territorial widespread distribution till to the
Provincial, Regional and National planning levels.
This answers to the necessity to divide the level of the
logical structuration of GIS, that’s to say the one
of the project of the GIS, from the one of data
acquisition and from the one of management.
Particularly the output of data entry can be directed on
Data Bank of high dimension by client-server systems
which allows the access to this data bank detached to the
Software of managing GIS. If the acquisition and analysis
levels of data is decentred, the management is entrusted
to the different planning level interested which warrant
the flexibility of using data: the modalities of
communications and the philosophy of the GIS on Network
is studied in the prototype levels.
The project is based on the experimentation of Network
connection typologies to create a prototype of
wine-viticulture Cadastral to manage agricultural
development planning, D.O.C. (Origin Controlled
Denomination Certificate) production and distributed
citizen services.
The first level is represented by the GIS model
prototype, (developed by the DIET Department of the
"UniversitÓ degli Studi di Pavia"), of the
"Wine-viticulture Cadastre and Register of Oliva
Gessi": the Commune of Oliva Gessi is the sample
zone chosen. The second level is the implementation of
the GIS model in ArcInfo, that could represent a GIS
model with widespread diffusion in the states and regions
or sub regions. To realize a wide level of managing the
agricultural activities it has been supposed a Network
Model to connect the different GIS built up from
different places and the related Data (third level).
LEVEL I
THE "WINE-VITICULTURE
CADASTRE AND REGISTER PROTOTYPE OF OLIVA GESSI"
THE REALIZATION OF THE FIRST
PROTOTYPE
The realization of a GIS prototype on the
wine-viticulture Cadastres was built up four years ago in
the University of Pavia, Faculty of Engineering,
Department of Ingegneria Edile e del Territorio (DIET).
The result represents the starting point, for the
development of the research carried on in co-operation
with the DIIAR Department of the Politecnico of Milan.
The core of the research is the connection between the
local level of managing also little and widespread
Wine-viticulture Cadastres to a world wide network level
of managing agricultural resources.
For the first apply it has been chosen the Commune of
Oliva Gessi like a sample zone of the research. In this
occasion data were managed with commercial Software
"CARIS" by Siemens. The Informative System of
the Wine-viticulture Cadastre and the Registry has been
realized to provide a valid instrument to support the
control, the watch over and the protection of the
production, of the trade and of the circulation of the
Wines, the must and the grapes.
At the national level there are lot of problems about the
administration of the areas and viticulture regions,
which form a relevant patrimony, both for the occupation
of soil (more then 1.200.000 hectares covered by
vineyards , that’s to say the four percent of the
national territory), and for socio-economic aspects.
Today’s tendency is that one to obtain quality
products and to promote certified products on qualified
characteristics.
The Policy of the CEE and now of the UE strongly
characterised and gave an impulse to the outline of the
agricultural production fixing the conditions and
determining the issue of laws, decrees and orders at the
national and European level to control, to defend and
protect the wine-viticulture activity and consequently to
reduce the frauds and the sophisticated products.
To this approach is also to sum the Policy of the CEE
which has influenced the soil management and use to avoid
an excessive exploitation of the soil use (Set Aside
Policies and related economic subsidies, etc.).
The research is strictly connected to the Region Policy
and receipt its main lines and directions. It has been
created in the past years an Informative System for the
Province of Pavia due to conform to the main lines of the
Regulation N.2392/86 of the European Community Council
and of the Regional Law of Lombardia (n.67 of 9/12/82)
which disciplines and regulates the institution and
maintenance of the wine-viticulture Cadastre and
Registry. With this role the Region delegated its own
powers to the Province Administrations and begun a policy
of devolution to obtain a system which could be used not
only like a control instrument but like a support to the
production, and therefore useful to the Administration
Government of the Communes, to the social co-operative
store for the sale of wine and for the production of
wine, to the association and to the single wine makers,
and at least to the consumers’ associations and
co-operatives.
GOALS AND DATA ORGANIZATION
The Informative System was developed with the following
aims:
- to give information about each
Cadastral parcels;
- to locate on the territory the
vineyards cultivated by the single farmers;
- to classify and catalogue for
each vineyard the kind of vines risen up, the
related surfaces, the year of establishment of
the production, the declaration and recognition
of the DOC certify with all the typical
parameters of a vineyard;
- to give the Registry data of
the owners and of the administrators.
ALFA-NUMERICAL DATA and ARCHIVES .
All the data has been put in a database organized in
different archives :
- The "ARCHIVIO
CATASTO" ("Cadastre" Archive)
- The "ARCHIVIO
ANAGRAFE" ("Registry" Archive)
- The "ARCHIVIO
VIGNETO" ("Vineyard" Archive)
The Archives has been set up under
simple data base software (Access) with their own
relationship (see the illustration table of attributes in
Fig. 1).
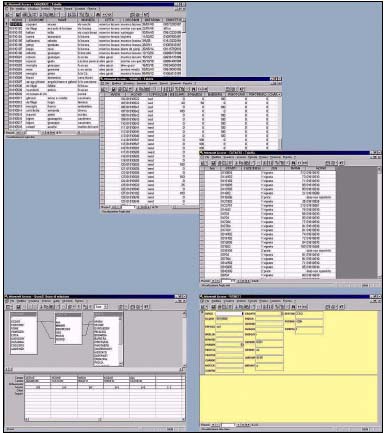
Figure 1
The data acquisition Mask, the Archives managed on Access
relationship and the query level
GEOGRAPHIC DATA. To relate all
these Archives in a GIS it has been acquired in different
phases the cartograpghic and environmental data to
describe the territory. The spatial references of the
descriptive data are at the base of a GIS.
It has been acquired in digital
format the different existing cartography :
- the Regional technical
Cartography at the scale 1 :10000;
- the Cadastral cartography at
the scale 1 :2000 of all the Commune
territory of Oliva Gessi;
- map projection transformation
from Cassini-Soldner to Gauss Boaga.
There is an Italian problem to
transform map projection of Cadastral Carthograpy which
use the Cassini-Soldner map projection to the Gauss Boaga
projection, used by Numerical Cartography.
It has been supposed a Standard Code System for all the
geometric entities of the numerical cartography. The
System of Codes has to be structured in base of the
classes of objects to be differentiated in the
cartography. To each entity is assigned an eight digit
field : to codify data in a flexible way, it has
been adopted a tree structure : the first two number
are the topic categories of elements (building,
hidrography, etc., the second two are about the typology
of he object, the others specify the typology of the
object related to the class.
The Standard Codes defined for the categories are the
following:
01 railway;
02 streets;
03 buildings;
04 rivers;
05 vegetation;
06 administrative limits;
07 contour level and orography;
08 point entity;
09 surfaces, quarries.
The Cartography has been updated by
the photointerpetation methodology. The
photointerpretation can be an useful instrument to
recognize the different kind of the growing (maize, corn,
grass, alfalfa, etc.) ; the aerial taken were
acquired by a AGFA HORIZON scanner (resolution 1200 dpi)
with three optically butted linear CCD Toshiba TDC 141
(3x500 pixel).
An integrant voice of the model is represented by the Map
of the soils destinations made parcels by parcels through
the photointerpretation.
GIS ON NETWORK
To realize a GIS at a wide level to manage the
agricultural activities of Regions, in Italy as in other
States, it would signify to build up standard structures
of Data acquisition, a data model enough flexible to be
applied to the different realities, query and analysis
levels to be managed on the heterogeneous data
(raster-vector, qualitative and descriptive data in the
form of attributes or tables of attributes, the different
cartographic projections with the methodology to
transform datum system one to each other, etc.) ; on
the other side it means to design a connection
architecture between the different data bank based on the
Relational Data Bank Management Systems and the different
GIS models built up in function of the different aims and
applies.
LEVEL II
THE GIS MODEL SUPPOSED FOR THE
WINE-VITICULTURE CADASTRE OF OLIVA GESSI IS IMPLEMENTED
WITH ARCINFO
It has been supposed and realized
different survey and representation levels strictly
related one to the other to improve the knowledge and to
describe the geometrical characteristics of all the
agricultural area. The connection to the Archives
("Catasto", "Anagrafe" and
"Vigneto") are managed in ArcInfo through SQL
connections to Access Data Bases (Fig. 2).
I. The survey data
acquisition :
- The project, simulation and
realisation of a network to hold the
photogrammetric restitution;
- The photogrammetric
restitution (Gauss Boaga) at the scale 1:10000 or
1:5000 (Technical Regional Cartography);
- The digital acquisition of the
Cadastral Cartography (Cassini Soldner);
- Ortophoto digital projection
obtained from the aerial takens.
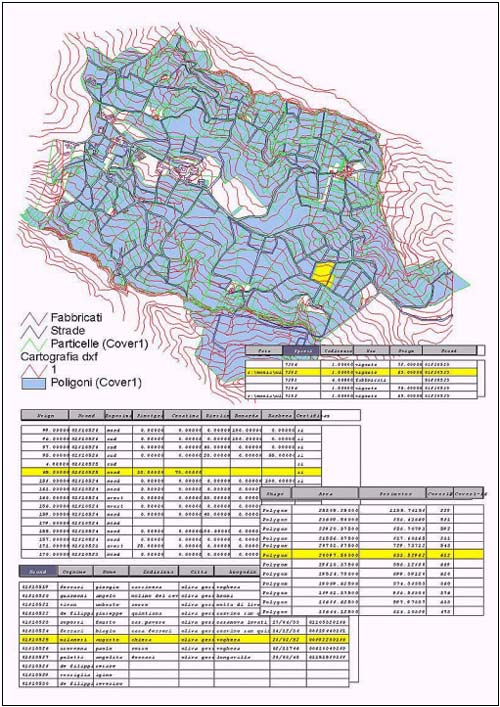
Figure 2
Wire connection to ArcInfo Cover and SQL connection to
the Archives from ArcView
II. Bidimensional and
three-dimensional geographic data management made by
ArcInfo
- Integration of the Regional
technical Cartography at the scale 1 :10000
- Integration of the Cadastral
cartography at the scale 1 :2000 of all the
Commune territory of Oliva Gessi in the Gauss
Boaga Cartography to relate Cadastral Cartography
to the photogrammetric restitution of the
numerical cartography; topological
reconstructions (PAT, AAT, PAT);
- Map projection transformation
from Cassini-Soldner to Gauss Boaga;
- Map projection transformation
from Gauss Boaga to UTM (for world wide
connection);
- Photointerpretation and map of
the soil use (Fig. 3);
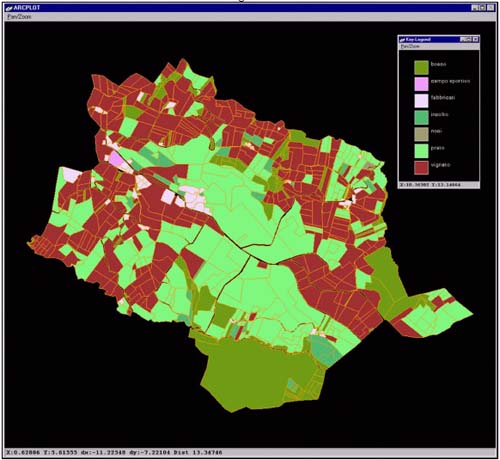
Figure 3
The map of the soil use of Oliva Gessi
- Generation of the TIN on the
elevation point obtained by the photogrammetric
restitutions and representation by contour
levels; generation of the Lattice with Grid of
2.5mt x 2.5mt;
- Projection of the Covers (the
parcels of properties from the Cadastral
Cartography, the codified entities from the
Numerical Cartography, streets, buildings, etc.)
on the 3D MESH (Fig. 4);
- Projection of the Ortophoto on
the parcels (Fig. 5) and on the 3D MESH built on
the Lattice (Fig. 6).
III. SQL connection with the
Archives Prototype upper described.
Recognition of the geometrical
parcels polygons with their annotation feature class and
automatical connection to the Numerical data banks of the
Archives, The "Cadastral" one, the
"Vineyard" one and the "Registry of
properties" one.
IV. Settlement of query System and
analysis functions made on the GIS model (Fig. 2).
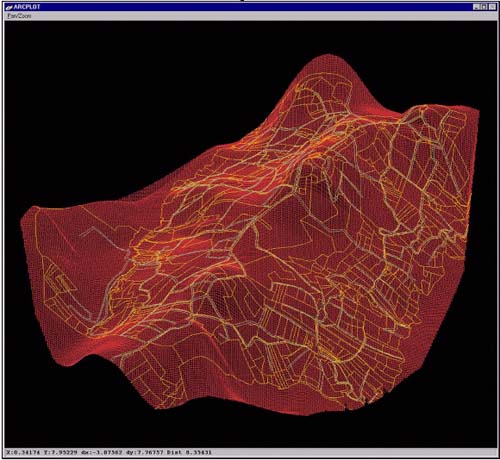
Figure 4
Projection of the Covers (the parcels of properties from
the Cadastral Cartography, the codified entities from the
Numerical Cartography, streets, buildings, etc.) on the
3D MESH
LEVEL III
GIS ON NETWORK TYPOLOGIES TO
MANAGE AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT PLANNING, D.O.C.
PRODUCTION OF THE WINE AND CITIZEN SERVICES
THE EXPERIMENTATION OF NETWORK
CONNECTION TYPOLOGIES TO MANAGE AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT
PLANNING AND D.O.C. PRODUCTION
Once realized the prototype inside ArcInfo the further
step is to suppose a Network model to connect different
GIS and Data management, built on the GIS
Wine-Viticulture Cadastres.
The project is based on the experimentation of Network
connection typologies to create a prototype of
wine-viticulture Cadastral to manage agricultural
development planning, D.O.C. (Origin Controlled
Denomination Certificate) production and distributed
citizen services.
Each wine-viticular GIS, once structured by the local
administrations with widespread diffusion on the
territory, allows to relate the different kinds of
species of wine to the geographical regions and
subregions, to access the level of production, to obtain
the training of marketing through geomarketing applies.
It becomes an important instrument to support the
decisions in agricultural development planning, to make
market forecast and budget, to project and quantify long
term and short-term investment with high
profitability : the last one can become a function
of complex query building project due to find the best
location of placements, the best suitable areas connected
to the transportation network capabilities, etc.
Therefore it becomes possible to control and to actively
protect the DOC production, the species and the wine
production in order to support controlled production
trends and resources allocation policies.
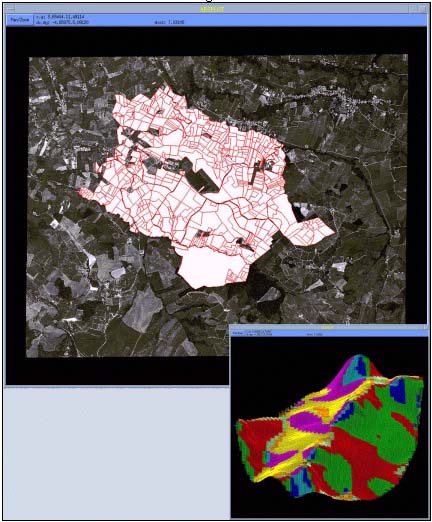
Figure 5
Projection of the Ortophoto on the parcels and 3D MESH
exposure map
Data acquisition and Management,
correlation between human activity and available
resources, govern of change and forecast are some of the
basic topics to guaranty the quality of a project.
For the High Level Decision Policies it’s mandatory
to use all the geographic informations derived from the
low level management. It’s mandatory to use
Geographic information to support, plan and forecast
economic trend, economic development, financial policies
of best suitable investment related to the depression
areas, to the natural resources, to the infrastructures
of the territory and to the geographical state of art
(that’s to say relate perhaps water resources and
access, communication network with technological network,
water pipes, etc.). All these aspect cannot be separately
treated, since they are strictly related once to the
other through logical connections which require an effort
to build congruent description in open systems. Therefore
for decision makers it’s important to use organized
information in a suitable GIS Data Bank Organization on
Network.
Remote access to Relational Data Bank: the remote access
to Relational Data Bank ‘global positioned’
using perhaps GIS SW as a client could be an useful
approach to support Economic – environmental Data
Management in this field of apply.
The Internet holds promise for exponential increases in
the efficiency and effectiveness of the ways in which we
obtain, use, and share geographic information in all its
forms (including maps, graphics, text and data).
Many extraordinary systems have already been built, and
over the next few years, an increasing number of GIS
application will "go on line".
ARCHITECTURES TO SUPPORT GIS DATA
BANK ORGANIZATION ON NETWORK
The geographical spatial temporal information updating is
required to avoid the redundancy and the efforts made to
collect data; for this purpose several client/server
Architectures (Fig. 7) can be designed for the data
transferring and remote management: on one side there are
Numerical Data Banks Servers (it will be tested the use
of RDBMS, relational Data Banks Model System, such as
Oracle and SQL link methodologies which run on
Line) : they can be accessed by a GIS Software (i.e.
ArcInfo used as a client) on the client side, but also by
Web Page through On Line GIS realized by a System query
tool (i.e. Map Object Internet Map Server); and in the
other side there are Geographical Data Bank Server to
manage millions of geographic objects with multi-access
connections on Network (i.e. SDE-Esri, SDO-Oracle).
The research has to improve type of net data handling
defined following different procedures: from GIS
Software, such as ArcInfo used as Client to connect to
the Remote Data Bank on different Servers till to the
Distributed Geographic Information System (DGI) on Line
to support citizens services through GIS tools developed
on WEB Servers by different Software.
The major developments are improving the interoperability
of servers and client software: SDE Spatial Data Base
Engine is an example of software support for additional
data types and new clients. Currently known for its
best-inclass retrieval of spatial shapes in a multi-user
environment, SDE is becoming the universal spatial
application server at many organizations world-wide.
The level of data acquisition, surveys and
representations, will be more and more differentiated
from the level of the information access. The level of
the information access can be differentiated due to the
typologies of users: from the virtual citizen service
windows to the specialised users. Client/Server
architecture would be the core of this "GIS Data
Bank Organization on Network". From the segretation
of data procedures, to the public domain access, in any
case it’s necessary to project network system of GIS
(on Internet or Intranet) determining standard
procedures, formats, protocols to make possible the free
transmission of data, limiting the loosing of time and
data knowledge and avoiding the duplication of the
efforts to collect data already acquired from everybody
else in the fixed rules.
DGI : DISTRIBUTED GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION CITIZEN SERVICES
Internet technology applies can be used to give people
access to geographic information in a variety of forms,
including maps, images, data sets, analysis operations,
queries and reports. Distributed Geographic Information
(DGI) is a term proposed to refer to this entire field;
that is the widespread (perhaps to a larger audience that
would have access using traditional GIS technology)
distribution of geographic information in different
forms.
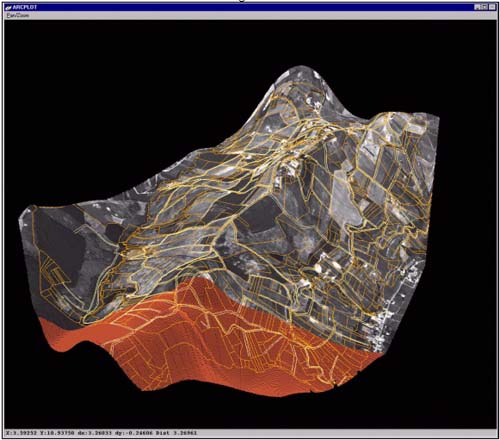

Figure 6
Projection of the Ortophoto on the 3D MESH built on the
Lattice with the parcels of the properties
DGI applications range from simple,
pre-drawn maps on a Web Page to network-based
collaborative GIS in which GIS users at remote locations
share common data and communicate with one another in
real time (not yet widely available). The technologies
being developed to make DGI applications possible include
servers (which store data and applications), and network
communications (which control the flow of information
between servers and clients).
The aim is to give users access to the full analysis
capabilities of your GIS. This would allow them to
perform complex multi-theme queries, create buffers and
customised maps, perform statistical spatial analysis,
and other tasks. This type of service allows the user to
create new data sets from their own analyses without
altering the data you maintain. The data sets the user
created could be stored on your server for their future
use or you might offer the option of downloading their
results as a map, report or raw data set.
MAP OBJECT INTERNET MAP SERVER TO
CREATE AN INTERACTIVE MAP BROWSER FOR THE
WINE-VITICULTURE CADASTRE’S GIS DATA ACCESS
MapObject Internet Map Server is an extension to the
MapObjects package, a collection of components for
building mapping and GIS applications. It can be used to
build a wide variety of dynamic mapping and GIS
applications, using any functionality in Map Objects
(which includes a large part of the functionality of
ArcInfo).
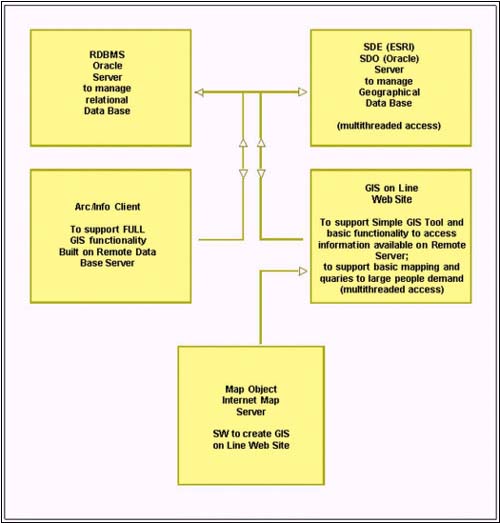
Figure 7
Multithreaded Architectures (many request processed
simultaneously)
to support GIS Data Bank Organization on Network
MapObject Internet Map Server is
used to create an interactive map browser for the
Wine-viticulture Cadastre’s GIS, including the
Geographic Data (parcels, TIN, MESH, etc.) and the
Alfa-numerical Archives (the properties, the registry,
the production and type of the Wines, etc.) which can be
managed in the future on the different Servers (Oracle
Servers, SDE-Servers, SDO-Servers) : when viewing
parcels, the user can plot a particular query and get
complete attribute information.
The interactive maps could allow citizens to have
information about the agricultural production area and
the widespread farm even the smaller one with the own
characteristics, the prices and the availability of the
wine (in function of the annual most important
production, of the sale network (from the mail-order
sailing, to the auction sale, to the cash sale or credit
cards modalities…).
REFERENCES
- Amerighi, M.C., Calculli, S.,
Galetto, R., Pietra, F., Rispoli, G., "La
realizzazione dello schedario vitivinicolo nella
Provincia di Pavia", In La gestione del
territorio viticolo sulla base delle zone
pedoclimatiche e del catasto. Logos
International, Pavia, 1991
- Galetto, R., Viola, F.,
"Il tempo come quarta dimensione della
cartografia numerica", BOLL. SIFET n.4, 1993
- Galetto, R., Spalla, A.,
Viola, F., "Realisation of a GIS prototype
for Air Pollution Monitoring and Mapping",
ISPRS International Archives of Photogrammetry
and Remote Sensing, Vol.30, 1994
- Monti, C., "Present
situation and Prospects in Italian Cadastral
Cartography", ELIS ’95 Seminar European
Land Information System, Kos, Greece, oktober,
1995
- Galetto, R., Spalla, A.,
"I Sistemi Informativi Territoriali per la
Gestione del territorio e
dell’ambiente", in Il Telerilevamento
ed i Sistemi Informativi Territoriali nella
gestione delle risorse ambientali. EUR16330,
Lussemburgo, 1995
- Brumana, R., Monti, C.,
"Relational model of managing data surveys
of complex and dynamic architectural manufacts of
masonry" , 11th International Brick/Block
Masonry Conference Tongji University, Shanghai
CHINA, 14-16 October 1997
- Monti, C., Brumana, R.,
Achille, C., Fregonese, L., "GIS to support
the planning, the management and the project of
conservation of Historical Centers", ISPRS
Commission V International Symposium on Real-Time
Imaging and Dynamic Analysis, Hakodate, Japan,
2-5 June, 1998
|

















